Analysis of multiply spliced transcripts in lymphoid tissue reservoirs of rhesus macaques infected with RT-SHIV during HAART
- PMID: 24505331
- PMCID: PMC3914874
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087914
Analysis of multiply spliced transcripts in lymphoid tissue reservoirs of rhesus macaques infected with RT-SHIV during HAART
"VSports app下载" Abstract
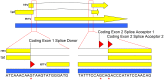
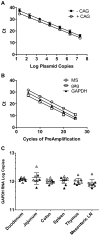
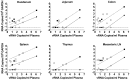
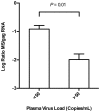
Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) can reduce levels of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) to undetectable levels in infected individuals, but the virus is not eradicated. The mechanisms of viral persistence during HAART are poorly defined, but some reservoirs have been identified, such as latently infected resting memory CD4⁺ T cells. During latency, in addition to blocks at the initiation and elongation steps of viral transcription, there is a block in the export of viral RNA (vRNA), leading to the accumulation of multiply-spliced transcripts in the nucleus. Two of the genes encoded by the multiply-spliced transcripts are Tat and Rev, which are essential early in the viral replication cycle and might indicate the state of infection in a given population of cells. Here, the levels of multiply-spliced transcripts were compared to the levels of gag-containing RNA in tissue samples from RT-SHIV-infected rhesus macaques treated with HAART. Splice site sequence variation was identified during development of a TaqMan PCR assay. Multiply-spliced transcripts were detected in gastrointestinal and lymphatic tissues, but not the thymus VSports手机版. Levels of multiply-spliced transcripts were lower than levels of gag RNA, and both correlated with plasma virus loads. The ratio of multiply-spliced to gag RNA was greatest in the gastrointestinal samples from macaques with plasma virus loads <50 vRNA copies per mL at necropsy. Levels of gag RNA and multiply-spliced mRNA in tissues from RT-SHIV-infected macaques correlate with plasma virus load. .
Conflict of interest statement (V体育ios版)
V体育平台登录 - Figures
References
-
- Poles MA, Boscardin WJ, Elliott J, Taing P, Fuerst MM, et al. (2006) Lack of decay of HIV-1 in gut-associated lymphoid tissue reservoirs in maximally suppressed individuals. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 43: 65–68. - PubMed
-
- Deeks SG, Wrin T, Liegler T, Hoh R, Hayden M, et al. (2001) Virologic and immunologic consequences of discontinuing combination antiretroviral-drug therapy in HIV-infected patients with detectable viremia. N Engl J Med 344: 472–480. - "VSports注册入口" PubMed
-
- Harrigan PR, Whaley M, Montaner JS (1999) Rate of HIV-1 RNA rebound upon stopping antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 13: F59–62. - PubMed
-
- Havlir DV, Bassett R, Levitan D, Gilbert P, Tebas P, et al. (2001) Prevalence and predictive value of intermittent viremia with combination hiv therapy. JAMA 286: 171–179. - PubMed (VSports app下载)
"VSports app下载" Publication types
- "V体育ios版" Actions
MeSH terms
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "VSports" Actions
Substances
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical (VSports在线直播)
Research Materials

