The levels of liver enzymes and atypical lymphocytes are higher in youth patients with infectious mononucleosis than in preschool children (VSports注册入口)
- PMID: 24459643
- PMCID: PMC3894438
- DOI: V体育2025版 - 10.3350/cmh.2013.19.4.382
"V体育官网" The levels of liver enzymes and atypical lymphocytes are higher in youth patients with infectious mononucleosis than in preschool children
"VSports" Abstract
Background/aims: Infectious mononucleosis (IM) is the clinical presentation of primary infection with Epstein-Barr virus VSports手机版. Although the literature contains a massive amount of information on IM, most of this is related specifically to only children or adults separately. In order to distinguish any differences between preschool children and youth patients, we retrospectively analyzed their demographic and clinical features. .
Methods: Records of patients hospitalized from December 2001 to September 2011 with a diagnosis of IM were retrieved from Peking University First Hospital, which is a tertiary teaching hospital in Beijing. The demographic data and clinical characteristics were collected. V体育安卓版.
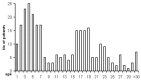
Results: IM was diagnosed in 287 patients during this 10-year period, with incidence peaks among preschool children (≤7 years old, 130/287, 45. 3%) and youth patients (>15 and <24 years old, 101/287, 35. 2%) V体育ios版. Although the complaints at admission did not differ between these two patient groups, the incidence of clinical signs (tonsillopharyngitis, lymphadenopathy, hepatomegaly, and edema of the eyelids) was much higher in preschool children. The incidence of liver lesion and percentage of atypical lymphocytes were significantly higher in the youth group (P<0. 001), and the average hospital stay was longer in this group. Pneumonia was the most common complication, and there was no case of mortality. .
Conclusions: The incidence of IM peaks among preschool children and youth patients in Beijing, China VSports最新版本. The levels of liver enzymes and atypical lymphocytes increase with age. .
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus; Infectious mononucleosis; Preschool children; Youth. V体育平台登录.
Conflict of interest statement (V体育ios版)
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Takeuchi K, Tanaka-Taya K, Kazuyama Y, Ito YM, Hashimoto S, Fukayama M, et al. Prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus in Japan: trends and future prediction. Pathol Int. 2006;56:112–116. - PubMed
-
- Kangro HO, Osman HK, Lau YL, Heath RB, Yeung CY, Ng MH. Seroprevalence of antibodies to human herpesviruses in England and Hong Kong. J Med Virol. 1994;43:91–96. - V体育官网入口 - PubMed
-
- Du HJ, Zhou L, Liu HT, Wang Q, Zhan SB, Jia ZY, et al. A serological survey of Epstein-Barr virus infection in children in Beijing. Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi. 2008;22:30–32. - PubMed
-
- Vouloumanou EK, Rafailidis PI, Falagas ME. Current diagnosis and management of infectious mononucleosis. Curr Opin Hematol. 2012;19:14–20. - PubMed
-
- Luzuriaga K, Sullivan JL. Infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1993–2000. - PubMed
"VSports注册入口" Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
"V体育平台登录" Full Text Sources
V体育官网 - Other Literature Sources
Medical