Human COX20 cooperates with SCO1 and SCO2 to mature COX2 and promote the assembly of cytochrome c oxidase
- PMID: 24403053
- PMCID: PMC4014192
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddu003 (VSports在线直播)
Human COX20 cooperates with SCO1 and SCO2 to mature COX2 and promote the assembly of cytochrome c oxidase
Abstract
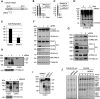
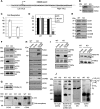
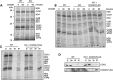
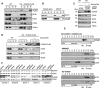
Cytochrome c oxidase (CIV) deficiency is one of the most common respiratory chain defects in patients presenting with mitochondrial encephalocardiomyopathies. CIV biogenesis is complicated by the dual genetic origin of its structural subunits, and assembly of a functional holoenzyme complex requires a large number of nucleus-encoded assembly factors. In general, the functions of these assembly factors remain poorly understood, and mechanistic investigations of human CIV biogenesis have been limited by the availability of model cell lines. Here, we have used small interference RNA and transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) technology to create knockdown and knockout human cell lines, respectively, to study the function of the CIV assembly factor COX20 (FAM36A). These cell lines exhibit a severe, isolated CIV deficiency due to instability of COX2, a mitochondrion-encoded CIV subunit. Mitochondria lacking COX20 accumulate CIV subassemblies containing COX1 and COX4, similar to those detected in fibroblasts from patients carrying mutations in the COX2 copper chaperones SCO1 and SCO2 VSports手机版. These results imply that in the absence of COX20, COX2 is inefficiently incorporated into early CIV subassemblies. Immunoprecipitation assays using a stable COX20 knockout cell line expressing functional COX20-FLAG allowed us to identify an interaction between COX20 and newly synthesized COX2. Additionally, we show that SCO1 and SCO2 act on COX20-bound COX2. We propose that COX20 acts as a chaperone in the early steps of COX2 maturation, stabilizing the newly synthesized protein and presenting COX2 to its metallochaperone module, which in turn facilitates the incorporation of mature COX2 into the CIV assembly line. .
Figures


References
-
- Shoubridge E.A. Cytochrome c oxidase deficiency. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2001;106:46–52. - PubMed (VSports手机版)
-
- Zee J.M., Glerum D.M. Defects in cytochrome oxidase assembly in humans: lessons from yeast. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006;84:859–869. - V体育官网入口 - PubMed
-
- Pecina P., Houstkova H., Hansikova H., Zeman J., Houstek J. Genetic defects of cytochrome c oxidase assembly. Physiol. Res. 2004;53:S213–S223. - PubMed
-
- Fontanesi F., Barrientos A. In: Mitochondrial Disorders Caused by Nuclear Genes. Part 3. Wong L.E., editor. New York: Springer Science; 2013. pp. 239–259. in press)
-
- Tsukihara T., Aoyama H., Yamashita E., Tomizaki T., Yamaguchi H., Shinzawa-Itoh K., Nakashima R., Yaono R., Yoshikawa S. The whole structure of the 13-subunit oxidized cytochrome c oxidase at 2.8 A. Science. 1996;272:1136–1144. - PubMed
"VSports手机版" Publication types
- Actions (V体育ios版)
MeSH terms
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
"VSports最新版本" Substances
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
Grants and funding (V体育安卓版)
LinkOut - more resources
"VSports手机版" Full Text Sources
"VSports注册入口" Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

