Morphological and functional characterization of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by a methionine-choline-deficient diet in C57BL/6 mice
- PMID: 24294355
- PMCID: PMC3843249
"V体育2025版" Morphological and functional characterization of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by a methionine-choline-deficient diet in C57BL/6 mice
Abstract
Background: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), appears to be increasingly common worldwide. Its histopathology and the effects of nutrition on liver function have not been fully determined. VSports手机版.
Aim: To elucidate the cellular mechanisms of NAFLD induced by a methionine-choline-deficient (MCD) diet in mice. Particular focus was placed on the role of phagocytic cells V体育安卓版. .
Methods: Male C57BL/6 mice were fed an MCD diet for 30 weeks. A recovery model was also established wherein a normal control diet was provided for 2 weeks after a period of 8, 16, or 30 weeks. V体育ios版.
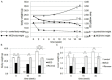
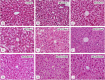
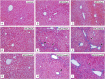
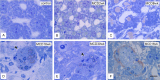
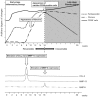
Results: Mice fed the MCD diet for ≥ 2 weeks exhibited severe steatohepatitis with elevated serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels. Steatohepatitis was accompanied by the infiltration of CD68-positive macrophages (Kupffer cells). The severity of steatohepatitis increased in the first 16 weeks but was seen to lessen by week 30. Fibrosis began to develop at 10 weeks and continued thereafter. Steatohepatitis and elevated serum hepatic enzyme concentrations returned to normal levels after switching the diet back to the control within the first 16 weeks, but fibrosis and CD68-positive macrophages remained VSports最新版本. .
Conclusions: The histopathological changes and irreversible fibrosis seen in this model were caused by prolonged feeding of an MCD diet. These results were accompanied by changes in the activity of CD68-positive cells with temporary elevation of CCL-2, MMP-13, and MMP-9 levels, all of which may trigger early steatohepatitis and late fibrosis through phagocytosis-associated MMP induction V体育平台登录. .
Keywords: CD68 antigen; Kupffer cells; liver fibrosis; matrix metalloproteinase (MMP); mouse; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) VSports注册入口. .
Figures (V体育官网入口)
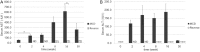


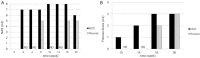


References
-
- Sanyal AJ. NASH: A global health problem. Hepatol Res. 2011;41:670–674. - PubMed
-
- Krawczyk M, Bonfrate L, Portincasa P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2010;24:695–708. - PubMed
-
- Mu YP, Ogawa T, Kawada N. Reversibility of fibrosis, inflammation, and endoplasmic reticulum stress in the liver of rats fed a methionine-choline-deficient diet. Lab Invest. 2010;90:245–256. - PubMed
-
- Lefkowitch JH, Haythe JH, Regent N. Kupffer cell aggregation and perivenular distribution in steatohepatitis. Mod Pathol. 2002;15:699–704. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育2025版)
MeSH terms (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
"V体育平台登录" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
