V体育官网入口 - A screen for hydroxymethylcytosine and formylcytosine binding proteins suggests functions in transcription and chromatin regulation
- PMID: 24156278
- PMCID: PMC4014808
- DOI: "V体育官网" 10.1186/gb-2013-14-10-r119
A screen for hydroxymethylcytosine and formylcytosine binding proteins suggests functions in transcription and chromatin regulation
Abstract (VSports在线直播)
Background: DNA methylation (5mC) plays important roles in epigenetic regulation of genome function. Recently, TET hydroxylases have been found to oxidise 5mC to hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), formylcytosine (5fC) and carboxylcytosine (5caC) in DNA. These derivatives have a role in demethylation of DNA but in addition may have epigenetic signaling functions in their own right. A recent study identified proteins which showed preferential binding to 5-methylcytosine (5mC) and its oxidised forms, where readers for 5mC and 5hmC showed little overlap, and proteins bound to further oxidation forms were enriched for repair proteins and transcription regulators VSports手机版. We extend this study by using promoter sequences as baits and compare protein binding patterns to unmodified or modified cytosine using DNA from mouse embryonic stem cell extracts. .
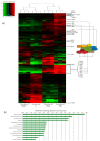
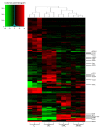
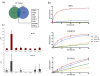
Results: We compared protein enrichments from two DNA probes with different CpG composition and show that, whereas some of the enriched proteins show specificity to cytosine modifications, others are selective for both modification and target sequences V体育安卓版. Only a few proteins were identified with a preference for 5hmC (such as RPL26, PRP8 and the DNA mismatch repair protein MHS6), but proteins with a strong preference for 5fC were more numerous, including transcriptional regulators (FOXK1, FOXK2, FOXP1, FOXP4 and FOXI3), DNA repair factors (TDG and MPG) and chromatin regulators (EHMT1, L3MBTL2 and all components of the NuRD complex). .
Conclusions: Our screen has identified novel proteins that bind to 5fC in genomic sequences with different CpG composition and suggests they regulate transcription and chromatin, hence opening up functional investigations of 5fC readers. V体育ios版.
Figures

References
-
- Tahiliani M, Koh KP, Shen Y, Pastor WA, Bandukwala H, Brudno Y, Agarwal S, Iyer LM, Liu DR, Aravind L, Rao A. Conversion of 5-methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mammalian DNA by MLL partner TET1. Science. 2009;14:930–935. doi: 10.1126/science.1170116. - "V体育官网入口" DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Khare T, Pai S, Koncevicius K, Pal M, Kriukiene E, Liutkeviciute Z, Irimia M, Jia PX, Ptak C, Xia MH, Tice R, Tochigi M, Morera S, Nazarians A, Belsham D, Wong AHC, Blencowe BJ, Wang SC, Kapranov P, Kustra R, Labrie V, Klimasauskas S, Petronis A. 5-hmC in the brain is abundant in synaptic genes and shows differences at the exon-intron boundary. Nat Struct Mole Biol. 2012;14:1037–U1094. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2372. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育官网" Actions
V体育2025版 - MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
Substances
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
Grants and funding
- 095645/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0700098/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- "V体育ios版" BB/H008071/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0801727/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- "VSports app下载" 6934/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
VSports - LinkOut - more resources
"V体育平台登录" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

