Viral RNA levels and env variants in semen and tissues of mature male rhesus macaques infected with SIV by penile inoculation
- PMID: 24146859
- PMCID: PMC3795772
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076367 (VSports手机版)
V体育ios版 - Viral RNA levels and env variants in semen and tissues of mature male rhesus macaques infected with SIV by penile inoculation
Abstract
HIV is shed in semen but the anatomic site of virus entry into the genital secretions is unknown. We determined viral RNA (vRNA) levels and the envelope gene sequence in the SIVmac 251 viral populations in the genital tract and semen of 5 adult male rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) that were infected after experimental penile SIV infection. Paired blood and semen samples were collected from 1-9 weeks after infection and the monkeys were necropsied eleven weeks after infection. The axillary lymph nodes, testes, epididymis, prostate, and seminal vesicles were collected and vRNA levels and single-genome analysis of the SIVmac251 env variants was performed. At the time of semen collection, blood vRNA levels were between 3 VSports手机版. 09 and 7. 85 log10 vRNA copies/ml plasma. SIV RNA was found in the axillary lymph nodes of all five monkeys and in 3 of 5 monkeys, all tissues examined were vRNA positive. In these 3 monkeys, vRNA levels (log10 SIVgag copies/ug of total tissue RNA) in the axillary lymph node (6. 48 ± 0. 50) were significantly higher than in the genital tract tissues: testis (3. 67 ± 2. 16; p<0. 05), epididymis (3. 08 ± 1. 19; p<0. 0001), prostate (3. 36 ± 1. 30; p<0. 01), and seminal vesicle (2. 67 ± 1. 50; p<0. 0001). Comparison of the SIVmac251 env viral populations in blood plasma, systemic lymph node, and genital tract tissues was performed in two of the macaques. Visual inspection of the Neighbor-Joining phylograms revealed that in both animals, all the sequences were generally distributed evenly among all tissue compartments. Importantly, viral populations in the genital tissues were not distinct from those in the systemic tissues. Our findings demonstrate striking similarity in the viral populations in the blood and male genital tract tissues within 3 months of penile SIV transmission. .
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

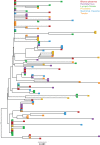

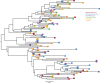
References
-
- Pillai SK, Good B, Pond SK, Wong JK, Strain MC, et al. (2005) Semen-specific genetic characteristics of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 env. J Virol 79: 1734–1742. - "V体育安卓版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Paranjpe S, Craigo J, Patterson B, Ding M, Barroso P, et al. (2002) Subcompartmentalization of HIV-1 quasispecies between seminal cells and seminal plasma indicates their origin in distinct genital tissues. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 18: 1271–1280. - VSports最新版本 - PubMed
-
- Curran R, Ball JK (2002) Concordance between semen-derived HIV-1 proviral DNA and viral RNA hypervariable region 3 (V3) envelope sequences in cases where semen populations are distinct from those present in blood. J Med Virol 67: 9–19. - PubMed
"VSports手机版" Publication types
"V体育安卓版" MeSH terms
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Substances
- "V体育官网" Actions
Associated data
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions
- Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- VSports - Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions
- Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions
- Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- VSports - Actions
- Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- VSports - Actions
- Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
Grants and funding
V体育官网入口 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

