Distinct antimicrobial peptide expression determines host species-specific bacterial associations
- PMID: 24003149
- PMCID: PMC3785777
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1304960110
V体育ios版 - Distinct antimicrobial peptide expression determines host species-specific bacterial associations
Abstract
Animals are colonized by coevolved bacterial communities, which contribute to the host's health. This commensal microbiota is often highly specific to its host-species, inferring strong selective pressures on the associated microbes. Several factors, including diet, mucus composition, and the immune system have been proposed as putative determinants of host-associated bacterial communities. Here we report that species-specific antimicrobial peptides account for different bacterial communities associated with closely related species of the cnidarian Hydra. Gene family extensions for potent antimicrobial peptides, the arminins, were detected in four Hydra species, with each species possessing a unique composition and expression profile of arminins. For functional analysis, we inoculated arminin-deficient and control polyps with bacterial consortia characteristic for different Hydra species and compared their selective preferences by 454 pyrosequencing of the bacterial microbiota. In contrast to control polyps, arminin-deficient polyps displayed decreased potential to select for bacterial communities resembling their native microbiota. This finding indicates that species-specific antimicrobial peptides shape species-specific bacterial associations. VSports手机版.
Keywords: Cnidaria; core microbiota; holobiont; host-microbe; phylosymbiotic V体育安卓版. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
"V体育官网入口" Figures

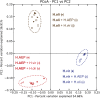
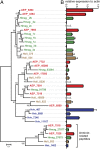
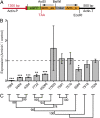

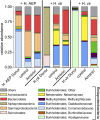
V体育官网 - References
-
- Ley RE, Lozupone CA, Hamady M, Knight R, Gordon JI. Worlds within worlds: Evolution of the vertebrate gut microbiota. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008;6(10):776–788. - "VSports" PMC - PubMed
-
- Douglas AE, Minto LB, Wilkinson TL. Quantifying nutrient production by the microbial symbionts in an aphid. J Exp Biol. 2001;204(Pt 2):349–358. - "V体育官网" PubMed
VSports - Publication types
- "VSports手机版" Actions
"VSports" MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育2025版)
Associated data
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育官网)
"V体育ios版" Other Literature Sources

