Protect and serve: Bcl-2 proteins as guardians and rulers of cancer cell survival
- PMID: 23974114
- PMCID: PMC3875667
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.25972
Protect and serve: Bcl-2 proteins as guardians and rulers of cancer cell survival
V体育安卓版 - Abstract
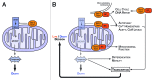
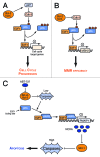
It is widely accepted that anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members promote cancer cell survival by binding to their pro-apoptotic counterparts, thereby preventing mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) and cytotoxic caspase activation. Yet, these proteins do not only function as guardians of mitochondrial permeability, preserving it, and maintaining cell survival in the face of acute or chronic stress, they also regulate non-apoptotic functions of caspases and biological processes beyond MOMP from diverse subcellular localizations and in complex with numerous binding partners outside of the Bcl-2 family. In particular, some of the non-canonical effects and functions of Bcl-2 homologs lead to an interplay with E2F-1, NFκB, and Myc transcriptional pathways, which themselves influence cancer cell growth and survival. We thus propose that, by feedback loops that we currently have only hints of, Bcl-2 proteins may act as rulers of survival signaling, predetermining the apoptotic threshold that they also directly scaffold. This underscores the robustness of the control exerted by Bcl-2 homologs over cancer cell survival, and implies that small molecules compounds currently used in the clinic to inhibit their mitochondrial activity may be not always be fully efficient to override this control. VSports手机版.
Keywords: Bcl-2 family; E2F-1; Myc; NF-κB; caspase. V体育安卓版.
Figures

References
-
- Tait SWG, Green DR. Mitochondria and cell death: outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:621–32. doi: 10.1038/nrm2952. - DOI (V体育官网) - PubMed
-
- Vo T-T, Ryan J, Carrasco R, Neuberg D, Rossi DJ, Stone RM, Deangelo DJ, Frattini MG, Letai A. Relative mitochondrial priming of myeloblasts and normal HSCs determines chemotherapeutic success in AML. Cell. 2012;151:344–55. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.038. - "VSports" DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- V体育ios版 - Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- VSports - Actions
- VSports - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
Substances
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
