Human circulating influenza-CD4+ ICOS1+IL-21+ T cells expand after vaccination, exert helper function, and predict antibody responses
- PMID: 23940329
- PMCID: PMC3761599
- DOI: V体育官网 - 10.1073/pnas.1311998110
Human circulating influenza-CD4+ ICOS1+IL-21+ T cells expand after vaccination, exert helper function, and predict antibody responses
Abstract
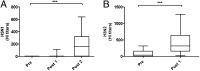
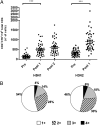
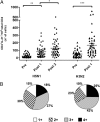
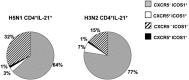
Protection against influenza is mediated by neutralizing antibodies, and their induction at high and sustained titers is key for successful vaccination. Optimal B cells activation requires delivery of help from CD4(+) T lymphocytes. In lymph nodes and tonsils, T-follicular helper cells have been identified as the T cells subset specialized in helping B lymphocytes, with interleukin-21 (IL-21) and inducible costimulatory molecule (ICOS1) playing a central role for this function. We followed the expansion of antigen-specific IL-21(+) CD4(+) T cells upon influenza vaccination in adults. We show that, after an overnight in vitro stimulation, influenza-specific IL-21(+) CD4(+) T cells can be measured in human blood, accumulate in the CXCR5(-)ICOS1(+) population, and increase in frequency after vaccination. The expansion of influenza-specific ICOS1(+)IL-21(+) CD4(+) T cells associates with and predicts the rise of functionally active antibodies to avian H5N1. We also show that blood-derived CXCR5(-)ICOS1(+) CD4(+) T cells exert helper function in vitro and support the differentiation of influenza specific B cells in an ICOS1- and IL-21-dependent manner. We propose that the expansion of antigen-specific ICOS1(+)IL-21(+) CD4(+) T cells in blood is an early marker of vaccine immunogenicity and an important immune parameter for the evaluation of novel vaccination strategies. VSports手机版.
Keywords: CD4 help; humoral response; predictivity. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors are employees of Novartis Vaccines and Diagnostics, Srl.
Figures

VSports - References
-
- Haining WN, Pulendran B. Identifying gnostic predictors of the vaccine response. Curr Opin Immunol. 2012;24(3):332–336. - PMC (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
-
- Galli G, et al. Adjuvanted H5N1 vaccine induces early CD4+ T cell response that predicts long-term persistence of protective antibody levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106(10):3877–3882. - PMC (V体育官网) - PubMed
-
- Vogelzang A, et al. A fundamental role for interleukin-21 in the generation of T follicular helper cells. Immunity. 2008;29(1):127–137. - PubMed
-
- Fazilleau N, Mark L, McHeyzer-Williams LJ, McHeyzer-Williams MG. Follicular helper T cells: Lineage and location. Immunity. 2009;30(3):324–335. - PMC (V体育2025版) - PubMed
Publication types (V体育ios版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
Substances
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
LinkOut - more resources
V体育2025版 - Full Text Sources
VSports在线直播 - Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

