"VSports手机版" Static mechanical stress induces apoptosis in rat endplate chondrocytes through MAPK and mitochondria-dependent caspase activation signaling pathways
- PMID: 23894471
- PMCID: PMC3716647
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069403
Static mechanical stress induces apoptosis in rat endplate chondrocytes through MAPK and mitochondria-dependent caspase activation signaling pathways (VSports)
Abstract
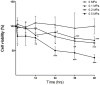
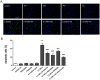
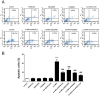
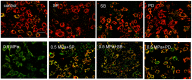
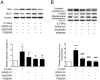
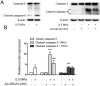
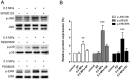
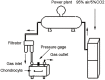
Mechanical stress has detrimental effects on cartilaginous endplate chondrocytes due to apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. In this study, we investigated the possible apoptosis signaling pathways induced by mechanical stress in cultured rat cervical endplate chondrocytes. Static mechanical load significantly reduced cell viability in a time- and load-dependent manner, as demonstrated by the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Chondrocyte apoptosis induced by mechanical stress was confirmed by annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) staining and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL). Western blot analysis revealed that static load-induced chondrocyte apoptosis was accompanied by increased phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). The loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm), increased Cytochrome c release, and activated Caspase-9 and Caspase-3, indicating that the mitochondrial pathway is involved in mechanical stress-induced chondrocyte apoptosis VSports手机版. Treatment with inhibitors of JNK (SP600125), p38 MAPK (SB203580), and ERK (PD98059) prior to mechanical stimulation reversed both the static load-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and the activation of JNK, p38 MAPK, and ERK. Taken together, the data presented in this study demonstrate that mechanical stress induces apoptosis in rat cervical endplate chondrocytes through the MAPK-mediated mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. .
Conflict of interest statement
Figures (VSports手机版)
References
-
- Ariga K, Miyamoto S, Nakase T, Okuda S, Meng W, et al. (2001) The relationship between apoptosis of endplate chondrocytes and aging and degeneration of the intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26: 2414–2420. - PubMed
-
- Lotz JC, Colliou OK, Chin JR, Duncan NA, Liebenberg E (1998) Compression-induced degeneration of the intervertebral disc: an in vivo mouse model and finite-element study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 23: 2493–2506. - PubMed (VSports app下载)
-
- Lotz JC, Chin JR (2000) Intervertebral disc cell death is dependent on the magnitude and duration of spinal loading. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 25: 1477–1483. - V体育官网入口 - PubMed
-
- Ariga K, Yonenobu K, Nakase T, Hosono N, Okuda S, et al. (2003) Mechanical stress-induced apoptosis of endplate chondrocytes in organ-cultured mouse intervertebral discs: an ex vivo study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 28: 1528–1533. - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Armada MJ, Carames B, Lires-Dean M, Cillero-Pastor B, Ruiz-Romero C, et al. (2006) Cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta, differentially regulate apoptosis in osteoarthritis cultured human chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 14: 660–669. - PubMed
"VSports手机版" Publication types
MeSH terms
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
V体育平台登录 - Substances
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
LinkOut - more resources (V体育2025版)
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (V体育2025版)
Research Materials (V体育官网入口)
Miscellaneous

