Neddylation plays an important role in the regulation of murine and human dendritic cell function
- PMID: 23863900
- PMCID: PMC3778550
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2013-02-486373
Neddylation plays an important role in the regulation of murine and human dendritic cell function
Abstract
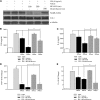
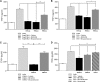
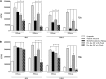
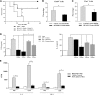
Posttranslational protein modifications (PTMs) are necessary for cells to function properly. The role of PTMs in regulating immune responses, specifically those mediated by dendritic cells (DCs), which are critical for both innate and adaptive immunity, is not well understood. Utilizing multiple but complementary approaches, we determined the role of an important but less understood type of PTM, namely, neddylation, in regulating DC functions. Inhibition of neddylation suppressed the release of proinflammatory cytokines by DCs in response to Toll-like receptor, nucleotide oligomerization domain-like receptor, and noninfectious CD40L stimulation. These effects were more profound than those mediated by the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib or a commonly used antiinflammatory agent, dexamethasone. Targeting neddylation also suppressed the ability of DCs to stimulate murine allogeneic T cells in vitro and in vivo and human allogeneic T-cell responses in vitro. Mechanistic studies demonstrated that inhibition of neddylation reduced both canonical and noncanonical nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activity. Neddylation inhibition prevented the degradation of inhibitor-κB and thus reduced the translocation and activation of NF-κB, but without perturbation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Thus, blocking neddylation could be a novel strategy for mitigating immune-mediated disease processes. VSports手机版.
Figures
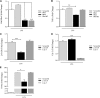
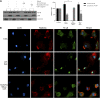
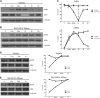
Comment in
-
The path(way) less traveled.Blood. 2013 Sep 19;122(12):1996-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-07-516856. Blood. 2013. PMID: 24052539
References
-
- Cloos PAC, Christgau S. Post-translational modifications of proteins: implications for aging, antigen recognition, and autoimmunity. Biogerontology. 2004;5(3):139–158. - PubMed
-
- Magnani M, Crinelli R, Bianchi M, Antonelli A. The ubiquitin-dependent proteolytic system and other potential targets for the modulation of nuclear factor-kB (NF-kB). Curr Drug Targets. 2000;1(4):387–399. - PubMed
-
- Hespel C, Moser M. Role of inflammatory dendritic cells in innate and adaptive immunity. Eur J Immunol. 2012;42(10):2535–2543. - V体育官网入口 - PubMed
"VSports" Publication types
- "V体育ios版" Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
Substances
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- VSports - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases (V体育安卓版)
Miscellaneous

