Increase of faecal tryptic activity relates to changes in the intestinal microbiome: analysis of Crohn's disease with a multidisciplinary platform
- PMID: 23840402
- PMCID: PMC3688706
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066074
Increase of faecal tryptic activity relates to changes in the intestinal microbiome: analysis of Crohn's disease with a multidisciplinary platform
Abstract
Objective: To investigate-by molecular, classical and functional methods-the microbiota in biopsies and faeces from patients with active Crohn's disease (CD) and controls VSports手机版. .
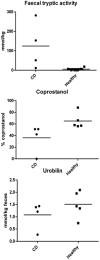
Design: The microbiota in biopsies was investigated utilizing a novel molecular method and classical cultivation technology V体育安卓版. Faecal samples were investigated by classical technology and four functional methods, reflecting alterations in short chain fatty acids pattern, conversion of cholesterol and bilirubin and inactivation of trypsin. .
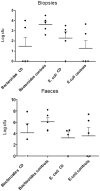
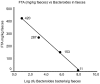
Results: By molecular methods we found more than 92% similarity in the microbiota on the biopsies from the two groups. However, 4 V体育ios版. 6% of microbes found in controls were lacking in CD patients. Furthermore, NotI representation libraries demonstrate two different clusters representing CD patients and controls, respectively. Utilizing conventional technology, Bacteroides (alt. Parabacteroides) was less frequently detected in the biopsies from CD patients than from controls. A similar reduction in the number of Bacteroides was found in faecal samples. Bacteroides is the only group of bacteria known to be able to inactivate pancreatic trypsin. Faecal tryptic activity was high in CD patients, and inversely correlated to the levels of Bacteroides. .
Conclusions: CD patients have compositional and functional alterations in their intestinal microbiota, in line with the global description hypothesis rather than the candidate microorganism theory. The most striking functional difference was high amount of faecal tryptic activity in CD patients, inversely correlated to the levels of Bacteroides in faeces. VSports最新版本.
"VSports在线直播" Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Dumonceau JM, Adler M, Cremer M, Van Gossum A (1994) The role of infectious agents in Crohn's disease. Acta Gastroenterol Belg 57 (5–6) 301–5. - PubMed
-
- Marteau P, Lepage P, Mangin I, Suau A, Doré J, et al. (2004) Review article: gut flora and inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther Suppl 4: 18–23. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (1997) Implementation of the WHO Global Strategy for Occupational Health for All. Plan of action: covering the specific period 1996–2001. Part 1 Int J Occup Med Environ Health 10 (2) 113–39. - PubMed
-
- Bergstrand LO, Gustafsson BE, Holmstrom B, Norin KE (1981) The physiological activity of human ileal flora in patients with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis evaluated by determination of germfree animal characteristics. Acta Chir Scand 147: 707–9. - "VSports" PubMed
-
- van der Merve JP, Mol GJJ (1982) Levels of trypsin and alpha-chymotrypsin in feces from patients with Crohn's disease. Digestion 24: 1–4. - PubMed
Publication types (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
MeSH terms (V体育官网)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
"V体育安卓版" Substances
- Actions (VSports手机版)
LinkOut - more resources (VSports在线直播)
"V体育安卓版" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

