A short protocol using dexamethasone and monophosphoryl lipid A generates tolerogenic dendritic cells that display a potent migratory capacity to lymphoid chemokines
- PMID: 23706017
- PMCID: PMC3674980
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-11-128
A short protocol using dexamethasone and monophosphoryl lipid A generates tolerogenic dendritic cells that display a potent migratory capacity to lymphoid chemokines
Abstract (VSports)
Background: Generation of tolerogenic dendritic cells (TolDCs) for therapy is challenging due to its implications for the design of protocols suitable for clinical applications, which means not only using safe products, but also working at defining specific biomarkers for TolDCs identification, developing shorter DCs differentiation methods and obtaining TolDCs with a stable phenotype. We describe here, a short-term protocol for TolDCs generation, which are characterized in terms of phenotypic markers, cytokines secretion profile, CD4+ T cell-stimulatory ability and migratory capacity. VSports手机版.
Methods: TolDCs from healthy donors were generated by modulation with dexamethasone plus monophosphoryl lipid A (MPLA-tDCs) V体育安卓版. We performed an analysis of MPLA-tDCs in terms of yield, viability, morphology, phenotypic markers, cytokines secretion profile, stability, allogeneic and antigen-specific CD4+ T-cell stimulatory ability and migration capacity. .
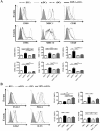
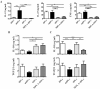
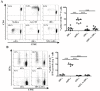
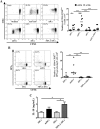
Results: After a 5-day culture, MPLA-tDCs displayed reduced expression of costimulatory and maturation molecules together to an anti-inflammatory cytokines secretion profile, being able to maintain these tolerogenic features even after the engagement of CD40 by its cognate ligand. In addition, MPLA-tDCs exhibited reduced capabilities to stimulate allogeneic and antigen-specific CD4+ T cell proliferation, and induced an anti-inflammatory cytokine secretion pattern. Among potential tolerogenic markers studied, only TLR-2 was highly expressed in MPLA-tDCs when compared to mature and immature DCs V体育ios版. Remarkable, like mature DCs, MPLA-tDCs displayed a high CCR7 and CXCR4 expression, both chemokine receptors involved in migration to secondary lymphoid organs, and even more, in an in vitro assay they exhibited a high migration response towards CCL19 and CXCL12. .
Conclusion: We describe a short-term protocol for TolDC generation, which confers them a stable phenotype and migratory capacity to lymphoid chemokines, essential features for TolDCs to be used as therapeutics for autoimmunity and prevention of graft rejection VSports最新版本. .
"V体育平台登录" Figures

References
-
- Randolph GJ, Ochando J, Partida-Sanchez S. Migration of dendritic cell subsets and their precursors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:293–316. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.26.021607.090254. - DOI (V体育安卓版) - PubMed
-
- Delgado-Martín C, Escribano C, Pablos JL, Riol-Blanco L, Rodríguez-Fernández JL. Chemokine CXCL12 Uses CXCR4 and a Signaling Core Formed by Bifunctional Akt, Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase (ERK)1/2, and Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 (mTORC1) Proteins to Control Chemotaxis and Survival Simultaneously in Mature Dendritic Cells. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:37222–37236. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.294116. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Torres-Aguilar H, Aguilar-Ruiz SR, González-Pérez G, Munguía R, Bajaña S, Meraz-Ríos MA, Sánchez-Torres C. Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells Generated with Different Immunosuppressive Cytokines Induce Antigen-Specific Anergy and Regulatory Properties in Memory CD4+ T Cells. J Immunol. 2010;184:1765–1775. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902133. - "VSports注册入口" DOI - PubMed
VSports最新版本 - Publication types
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
"V体育安卓版" MeSH terms
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
Substances
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
"V体育ios版" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

