V体育2025版 - Calcium-activated and apoptotic phospholipid scrambling induced by Ano6 can occur independently of Ano6 ion currents
- PMID: 23618909
- PMCID: PMC3668637
- DOI: "V体育官网入口" 10.1038/cddis.2013.135
"VSports app下载" Calcium-activated and apoptotic phospholipid scrambling induced by Ano6 can occur independently of Ano6 ion currents
Abstract
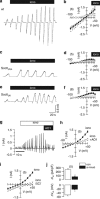
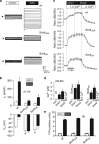
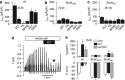
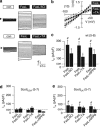
Immune cells and platelets maintain plasma membrane phospholipid asymmetry. Upon activation, this asymmetry is disrupted by phospholipid scrambling (PS), which is a major step during activation of immune cells, hemostasis and apoptosis. Anoctamin 6 (Ano6; TMEM16F) causes chloride (Cl(-)) and cation currents and is required for Ca(2+)-dependent PS. It is defective in blood cells from patients with Scott syndrome, a rare bleeding disorder. We examined if Cl(-) currents and PS are related, whether both processes are Ca(2+) dependent, and whether Ca(2+)-independent scrambling during intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis is controlled by Ano6. Ca(2+) increase by ionomycin activated Ano6 Cl(-) currents and PS in normal lymphocytes, but not in B-lymphocytes from two different patients with Scott syndrome. Fas ligand (FasL) did not increase intracellular Ca(2+), but activated Cl(-) currents in normal but not in Scott lymphocytes. Whole-cell currents were inhibited by Cl(-) channel blockers and by siRNA knockdown of Ano6 VSports手机版. In contrast, intrinsic mitochondrial apoptosis by ABT-737 did not induce Cl(-) currents in lymphocytes. PS was not inhibited by blockers of Ano6 or removal of Cl(-) ions. Remarkably, Ca(2+)-independent scrambling due to extrinsic (FasL) or intrinsic (ABT-737) apoptosis was unchanged in Scott cells. We conclude that: (i) Ano6 Cl(-) currents are activated by increase in cytosolic Ca(2+), or Ca(2+) independent by stimulation of Fas receptors; (ii) Ca(2+)-dependent PS induced by Ano6 does not require Cl(-) currents; (iii) Ca(2+)-independent PS does not require Ano6; (iv) Ano6 is necessary for Ca(2+)-dependent PS, but not by increasing intracellular Ca(2+). .
Figures
References
-
- Yang YD, Cho H, Koo JY, Tak MH, Cho Y, Shim WS, et al. TMEM16A confers receptor-activated calcium-dependent chloride conductance. Nature. 2008;455:1210–1215. - PubMed
-
- Caputo A, Caci E, Ferrera L, Pedemonte N, Barsanti C, Sondo E, et al. TMEM16A, a membrane protein associated with calcium-dependent chloride channel activity. Science. 2008;322:590–594. - PubMed
-
- Tian Y, Schreiber R, Kunzelmann K. Anoctamins are a family of Ca2+ activated Cl- channels. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:4991–4998. - PubMed
-
- Ferrera L, Caputo A, Galietta LJ. TMEM16A protein: a new identity for Ca(2+)-dependent Cl channels. Physiology. 2010;25:357–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
Substances
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
V体育2025版 - Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports在线直播" Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

