The role of pattern recognition receptors in intestinal inflammation
- PMID: 23515136
- PMCID: PMC3730813 (VSports app下载)
- DOI: "V体育官网入口" 10.1038/mi.2013.13
The role of pattern recognition receptors in intestinal inflammation
"VSports在线直播" Abstract
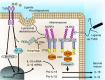
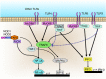
Recognition of microorganisms by pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) is the primary component of innate immunity that is responsible for the maintenance of host-microbial interactions in intestinal mucosa. Dysregulation in host-commensal interactions has been implicated as the central pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which predisposes to developing colorectal cancer. Recent animal studies have begun to outline some unique physiology and pathology involving each PRR signaling in the intestine. The major roles played by PRRs in the gut appear to be the regulation of the number and the composition of commensal bacteria, epithelial proliferation, and mucosal permeability in response to epithelial injury. In addition, PRR signaling in lamina propria immune cells may be involved in induction of inflammation in response to invasion of pathogens. Because some PRR-deficient mice have shown variable susceptibility to colitis, the outcome of intestinal inflammation may be modified depending on PRR signaling in epithelial cells, immune cells, and the composition of commensal flora. Through recent findings in animal models of IBD, this review will discuss how abnormal PRR signaling may contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammation and inflammation-associated tumorigenesis in the intestine VSports手机版. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures (V体育官网)
References
-
- Watts C, West MA, Zaru R. TLR signalling regulated antigen presentation in dendritic cells. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010;22:124–130. - PubMed (VSports在线直播)
-
- DeFranco AL, Rookhuizen DC, Hou B. Contribution of Toll-like receptor signaling to germinal center antibody responses. Immunol. Rev. 2012;247:64–72. - "VSports" PMC - PubMed
-
- Otte JM, Cario E, Podolsky DK. Mechanisms of cross hyporesponsiveness to Toll-like receptor bacterial ligands in intestinal epithelial cells. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:1054–1070. - PubMed
Publication types
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
"V体育2025版" MeSH terms
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
Substances
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
"VSports手机版" Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports手机版" Other Literature Sources
Medical

