Dendritic cells loaded with FK506 kill T cells in an antigen-specific manner and prevent autoimmunity in vivo
- PMID: 23390586
- PMCID: PMC3564474
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.00105
VSports手机版 - Dendritic cells loaded with FK506 kill T cells in an antigen-specific manner and prevent autoimmunity in vivo
Abstract
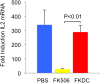
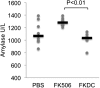
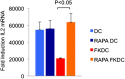
FK506 (Tacrolimus) is a potent inhibitor of calcineurin that blocks IL2 production and is widely used to prevent transplant rejection and treat autoimmunity. FK506 treatment of dendritic cells (FKDC) limits their capacity to stimulate T cell responses. FK506 does not prevent DC survival, maturation, or costimulatory molecule expression, suggesting that the limited capacity of FKDC to stimulate T cells may be due to inhibition of calcineurin signaling in the DC. Instead, we demonstrate that DC inhibit T cells by sequestering FK506 and continuously releasing the drug over several days. T cells encountering FKDC proliferate but fail to upregulate the survival factor bcl-xl and die, and IL2 restores both bcl-xl and survival VSports手机版. In mice, FKDC act in an antigen-specific manner to inhibit T-cell mediated autoimmune arthritis. This establishes that DCs can act as a cellular drug delivery system to target antigen specific T cells. DOI:http://dx. doi. org/10. 7554/eLife. 00105. 001. .
Keywords: FK506; Human; Mouse; autoimmunity; dendritic cells; drug delivery; rheumatoid arthritis. V体育安卓版.
Conflict of interest statement
Robert B Darnell. Reviewing editor,
The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
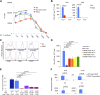
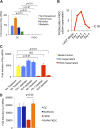
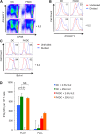
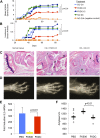
References (VSports app下载)
-
- Akbar AN, Borthwick NJ, Wickremasinghe RG, Panayoitidis P, Pilling D, Bofill M, et al. 1996. Interleukin-2 receptor common gamma-chain signaling cytokines regulate activated T cell apoptosis in response to growth factor withdrawal: selective induction of anti-apoptotic (bcl-2, bcl-xL) but not pro-apoptotic (bax, bcl-xS) gene expression. Eur J Immunol 26:294–9 - PubMed
-
- Albert ML, Sauter B, Bhardwaj N. 1998. Dendritic cells acquire antigen from apoptotic cells and induce class I-restricted CTLs. Nature 392:86–9 - PubMed
-
- Bendele A, McComb J, Gould T, McAbee T, Sennello G, Chlipala E, et al. 1999. Animal models of arthritis: relevance to human disease. Toxicol Pathol 27:134–42 - PubMed
-
- Brand DD, Latham KA, Rosloniec EF. 2007. Collagen-induced arthritis. Nat Protoc 2:1269–75 - "VSports" PubMed
Publication types
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
MeSH terms
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
Substances
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"V体育2025版" Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
