Biosurfactants in agriculture
- PMID: 23280539
- PMCID: PMC3555348
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-012-4641-8
Biosurfactants in agriculture (V体育平台登录)
VSports在线直播 - Abstract
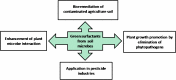
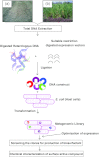
Agricultural productivity to meet growing demands of human population is a matter of great concern for all countries. Use of green compounds to achieve the sustainable agriculture is the present necessity. This review highlights the enormous use of harsh surfactants in agricultural soil and agrochemical industries. Biosurfactants which are reported to be produced by bacteria, yeasts, and fungi can serve as green surfactants. Biosurfactants are considered to be less toxic and eco-friendly and thus several types of biosurfactants have the potential to be commercially produced for extensive applications in pharmaceutical, cosmetics, and food industries. The biosurfactants synthesized by environmental isolates also has promising role in the agricultural industry. Many rhizosphere and plant associated microbes produce biosurfactant; these biomolecules play vital role in motility, signaling, and biofilm formation, indicating that biosurfactant governs plant-microbe interaction. In agriculture, biosurfactants can be used for plant pathogen elimination and for increasing the bioavailability of nutrient for beneficial plant associated microbes. Biosurfactants can widely be applied for improving the agricultural soil quality by soil remediation. These biomolecules can replace the harsh surfactant presently being used in million dollar pesticide industries. Thus, exploring biosurfactants from environmental isolates for investigating their potential role in plant growth promotion and other related agricultural applications warrants details research VSports手机版. Conventional methods are followed for screening the microbial population for production of biosurfactant. However, molecular methods are fewer in reaching biosurfactants from diverse microbial population and there is need to explore novel biosurfactant from uncultured microbes in soil biosphere by using advanced methodologies like functional metagenomics. .
Figures
References
-
- Abbasi H, Hamedi MM, Lotfabad TB, Zahiri HS, Sharafi H, Masoomi F, Moosavi-Movahedi AA, Ortiz A, Amanlou M, Noghabi KA. Biosurfactant-producing bacterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa MA01 isolated from spoiled apples: physicochemical and structural characteristics of isolated biosurfactant. J Biosci Bioeng. 2012;113:211–219. - PubMed
-
- Amani H, Mehrnia MR, Sarrafzadeh MH, Haghighi M, Soudi MR. Scale up and application of biosurfactant from Bacillus subtilis in enhanced oil recovery. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2010;162:510–523. - PubMed (VSports在线直播)
-
- Amaral PF, Coelho MA, Marrucho IM, Coutinho JA. Biosurfactants from yeasts: characteristics, production and application. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;672:236–249. - PubMed
-
- Andersen JB, Koch B, Nielsen TH, Sørensen D, Hansen M, Nybroe O, Christophersen C, Sørensen J, Molin S, Givskov M. Surface motility in Pseudomonas sp. DSS73 is required for efficient biological containment of the root-pathogenic microfungi Rhizoctonia solani and Pythium ultimum. Microbiol. 2003;149:37–46. - "VSports在线直播" PubMed
-
- Aşçi Y, Nurbaş M, Açikel YS. A comparative study for the sorption of Cd(II) by K-feldspar and sepiolite as soil components and the recovery of Cd(II) using rhamnolipid biosurfactant. J Environ Manage. 2008;88:383–392. - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育2025版" Actions
MeSH terms
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
Substances
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
V体育官网入口 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources