Diet, physical activity, and body composition changes during the first year of treatment for childhood acute leukemia and lymphoma
- PMID: 23211695
- PMCID: PMC3606649
- DOI: 10.1097/MPH.0b013e318279cd3e
Diet, physical activity, and body composition changes during the first year of treatment for childhood acute leukemia and lymphoma
Abstract
Background: Children who undergo treatment for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and lymphoma are at risk for several long-term health problems VSports手机版. Obesity, for which survivors of ALL and lymphoma are also at risk, may further exacerbate these problems. This pilot study evaluates changes in physical activity and body composition among children being treated for ALL and lymphoma and their parents. .
Procedures: Recently diagnosed adolescent ALL and lymphoma patients were recruited from 2 pediatric hematology and oncology clinics, and matched on age, race, and sex to healthy individuals in the community. Changes in diet, physical activity, and body composition were collected at baseline, 6, and 12 months V体育安卓版. .
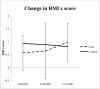
Results: All children (n=15) were, on average, 10 V体育ios版. 3 years of age at enrollment, and were fairly evenly distributed with regard to sex. Analyses revealed a significant difference between cases and controls with respect to the change in body mass index from baseline to 12 months (P=0. 01). In addition, controls demonstrated a significantly greater increase in moderate-vigorous physical activity than the cases [229. 8 metabolic equivalent of tasks (METs) vs. 23. 5 METs]; indicating cases remained fairly inactive over the course of treatment. .
Conclusions: Our data corroborate previous findings that following treatment for ALL and lymphoma, childhood cancer survivors tend to be less active and at greater risk for obesity than their healthy peers. The present study, which assessed cases prospectively over a 12-month period during the early phases of treatment, extends prior reports by demonstrating that these outcomes are evident at an early stage in treatment. VSports最新版本.
Figures
"VSports" References
-
- Didi M, Didcock E, Davies HA, Ogilvy-Stuart AL, Wales JK, Shalet SM. High incidence of obesity in young adults after treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in childhood. J Pediatr. 1995;127(1):63–7. - PubMed
-
- Mayer EI, Reuter M, Dopfer RE, Ranke MB. Energy expenditure, energy intake and prevalence of obesity after therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia during childhood. Horm Res. 2000;53(4):193–9. - V体育安卓版 - PubMed
-
- Schell MJ, Ochs JJ, Schriock EA, Carter M. A method of predicting adult height and obesity in long-term survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 1992;10(1):128–33. - PubMed
-
- Shaw MP, Bath LE, Duff J, Kelnar CJ, Wallace WH. Obesity in leukemia survivors: the familial contribution. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2000;17(3):231–7. - VSports - PubMed
-
- Withycombe JS, Post-White JE, Meza JL, Hawks RG, Smith LM, Sacks N, et al. Weight patterns in children with higher risk ALL: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group (COG) for CCG 1961. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2009;53(7):1249–54. Epub 2009/08/19. - V体育官网 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
"VSports最新版本" Grants and funding
"VSports app下载" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports注册入口" Other Literature Sources
Medical (VSports app下载)