Bortezomib added to daunorubicin and cytarabine during induction therapy and to intermediate-dose cytarabine for consolidation in patients with previously untreated acute myeloid leukemia age 60 to 75 years: CALGB (Alliance) study 10502
- PMID: 23129738
- PMCID: V体育官网 - PMC3577952
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2012.45.2177
Bortezomib added to daunorubicin and cytarabine during induction therapy and to intermediate-dose cytarabine for consolidation in patients with previously untreated acute myeloid leukemia age 60 to 75 years: CALGB (Alliance) study 10502
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to determine remission induction frequency when bortezomib was combined with daunorubicin and cytarabine in previously untreated older adults with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and safety of bortezomib in combination with consolidation chemotherapy consisting of intermediate-dose cytarabine (Int-DAC). VSports手机版.
Patients and methods: Ninety-five adults (age 60 to 75 years; median, 67 years) with previously untreated AML (including therapy-related and previous myelodysplastic syndrome) received bortezomib 1. 3 mg/m(2) intravenously (IV) on days 1, 4, 8, and 11 with daunorubicin 60 mg/m(2) on days 1 through 3 and cytarabine 100 mg/m(2) by continuous IV infusion on days 1 through 7. Patients who achieved complete remission (CR) received up to two courses of consolidation chemotherapy with cytarabine 2 gm/m(2) on days 1 through 5 with bortezomib. Three cohorts with escalating dose levels of bortezomib were tested (0. 7, 1. 0, and 1. 3 mg/m(2)). Dose-limiting toxicities were assessed during the first cycle of consolidation. The relationship between cell surface expression of CD74 and clinical outcome was assessed V体育安卓版. .
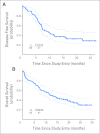
Results: Frequency of CR was 65% (62 of 95), and 4% of patients (four of 95) achieved CR with incomplete platelet recovery (CRp). Eleven patients developed grade 3 sensory neuropathy. Bortezomib plus Int-DAC proved tolerable at the highest dose tested. Lower CD74 expression was associated with CR/CRp (P = . 04) but not with disease-free or overall survival V体育ios版. .
Conclusion: The addition of bortezomib to standard 3 + 7 daunorubicin and cytarabine induction chemotherapy for AML resulted in an encouraging remission rate VSports最新版本. The maximum tested dose of bortezomib administered in combination with Int-DAC for remission consolidation was 1. 3 mg/m(2) and proved tolerable. Further testing of this regimen is planned. .
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures (V体育官网)

References
-
- Castaigne S, Chevret S, Archimbaud E, et al. Randomized comparison of double induction and timed-sequential induction to a “3 + 7” induction in adults with AML: Long-term analysis of the Acute Leukemia French Association (ALFA) 9000 study. Blood. 2004;104:2467–2474. - PubMed
-
- Burnett AK, Milligan D, Goldstone A, et al. The impact of dose escalation and resistance modulation in older patients with acute myeloid leukaemia and high risk myelodysplastic syndrome: The results of the LRF AML14 trial. Br J Haematol. 2009;145:318–332. - PubMed (VSports注册入口)
-
- Brunnberg U, Mohr M, Noppeney R, et al. Induction therapy of AML with ara-C plus daunorubicin versus ara-C plus gemtuzumab ozogamicin: A randomized phase II trial in elderly patients. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:990–996. - PubMed
-
- Adams J, Palombella VJ, Sausville EA, et al. Proteasome inhibitors: A novel class of potent and effective antitumor agents. Cancer Res. 1999;59:2615–2622. - PubMed
-
- Guzman ML, Neering SJ, Upchurch D, et al. Nuclear factor-kappaB is constitutively activated in primitive human acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Blood. 2001;98:2301–2307. - V体育官网 - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
MeSH terms
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
Substances (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports - Actions
Grants and funding
- CA33601/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States (VSports注册入口)
- CA32291/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States (VSports)
- U10 CA077597/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States (V体育平台登录)
- U10 CA059518/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045418/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA101140/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA041287/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA047559/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA77658/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States (VSports在线直播)
- U10 CA047642/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5K23CA118419-05/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States (V体育2025版)
- U10 CA047577/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA140148/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA032291/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- VSports手机版 - CA16058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA101140/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077658/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA41287/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035279/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States (V体育2025版)
- CA03927/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA031946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA033601/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA59518/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA47559/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- VSports手机版 - CA31946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 CA118419/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- "VSports手机版" U10 CA003927/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
V体育平台登录 - Miscellaneous

