Type I interferon response and innate immune sensing of cancer
- PMID: 23122052
- PMCID: "V体育官网" PMC3565059
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2012.10.004
Type I interferon response and innate immune sensing of cancer
Abstract
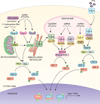
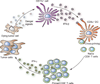
Unexpectedly, many cancers appear to induce a spontaneous adaptive T cell response. The presence of a T cell infiltrate has been linked to favorable clinical outcome in multiple cancer types. However, the innate immune pathways that bridge to an adaptive immune response under sterile conditions are poorly understood. Recent data have indicated that tumors can induce type I interferon (IFN) production by host antigen-presenting cells (APCs), which is required for a spontaneous T cell response in vivo. The innate immune sensing pathways that trigger type I IFN production are being elucidated VSports手机版. Host type I IFNs are also required for optimal therapeutic efficacy with radiation. This recently uncovered role for host type I IFNs for antitumor immunity has important fundamental and clinical implications. .
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd V体育安卓版. All rights reserved. .
Figures
References
-
- Pestka S, et al. Interferons, interferon-like cytokines, and their receptors. Immunol Rev. 2004;202:8–32. - "VSports注册入口" PubMed
-
- Stark GR, et al. How cells respond to interferons. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:227–264. - PubMed
-
- Jensen KE, et al. Interferon Responses of Chick Embryo Fibroblasts to Nucleic Acids and Related Compounds. Nature. 1963;200:433–434. - PubMed
-
- van den Broek MF, et al. Immune defence in mice lacking type I and/or type II interferon receptors. Immunol Rev. 1995;148:5–18. - PubMed
-
- Muller U, et al. Functional role of type I and type II interferons in antiviral defense. Science. 1994;264:1918–1921. - PubMed
Publication types (VSports注册入口)
MeSH terms
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
Substances
- "V体育官网" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources (V体育官网入口)
"V体育官网" Full Text Sources
V体育官网入口 - Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

