VSports app下载 - Early insulin glycemic control combined with tPA thrombolysis reduces acute brain tissue damages in a focal embolic stroke model of diabetic rats
- PMID: 23117722
- PMCID: PMC3600418
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.663476
Early insulin glycemic control combined with tPA thrombolysis reduces acute brain tissue damages in a focal embolic stroke model of diabetic rats
Abstract
Background and purpose: Therapeutic effects of early insulin glycemic control for poststroke hyperglycemia in combination with tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) thrombolytic therapy have not yet been studied but are of great clinical interest VSports手机版. In this study, we tested the effects of insulin plus tPA combination in a model of focal embolic stroke in Type I diabetic rats. .
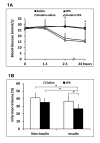
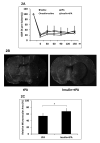
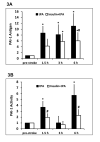
Methods: Streptozotocin was used to produce Type I diabetes in male Wistar rats for 6 weeks and then embolic focal strokes were induced. All rats were treated with insulin or saline at 1 hour followed by tPA or saline at 1. 5 hour after stroke. Mortality, infarction, hemispheric swelling, hemorrhagic transformation, and perfusion defects were examined at 24 hours after stroke. Total plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 antigen and activity levels were measured before stroke and 1. 5, 3, and 6 hours after stroke by ELISA. V体育安卓版.
Results: Early insulin glycemic control alone or tPA thrombolysis alone had no significant effects on ischemic infarction. However, early insulin glycemic control combined with tPA significantly reduced brain infarction and swelling, ameliorated tPA-associated hemorrhagic transformation, and improved plasma perfusion at 24 hours after stroke. We also found that the combination significantly decreased plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 antigen level at 6 hours and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 activity at 1 V体育ios版. 5 and 6 hours after stroke. .
Conclusions: Early insulin glycemic control may be beneficial in combination with tPA thrombolysis for ischemic stroke with diabetes mellitus or poststroke hyperglycemia. VSports最新版本.
Figures

References
-
- Allport L, Baird T, Butcher K, Macgregor L, Prosser J, Colman P, et al. Frequency and temporal profile of poststroke hyperglycemia using continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:1839–1844. - VSports app下载 - PubMed
-
- Kruyt ND, Biessels GJ, Devries JH, Roos YB. Hyperglycemia in acute ischemic stroke: Pathophysiology and clinical management. Nat Rev Neurol. 2010;6:145–155. - PubMed
-
- Bruno A, Kent TA, Coull BM, Shankar RR, Saha C, Becker KJ, et al. Treatment of hyperglycemia in ischemic stroke (this): A randomized pilot trial. Stroke. 2008;39:384–389. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed N, Davalos A, Eriksson N, Ford GA, Glahn J, Hennerici M, et al. Association of admission blood glucose and outcome in patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis: Results from the safe implementation of treatments in stroke international stroke thrombolysis register (sits-istr) Archives of neurology. 2010;67:1123–1130. - PubMed
Publication types
- Actions (V体育ios版)
MeSH terms (VSports)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- VSports - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
Substances
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources (V体育ios版)
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

