"VSports最新版本" A divalent interaction between HPS1 and HPS4 is required for the formation of the biogenesis of lysosome-related organelle complex-3 (BLOC-3)
- PMID: 23103514
- PMCID: VSports最新版本 - PMC3556189
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.10.019
A divalent interaction between HPS1 and HPS4 is required for the formation of the biogenesis of lysosome-related organelle complex-3 (BLOC-3) (VSports手机版)
"V体育平台登录" Abstract
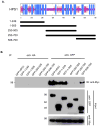
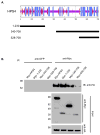
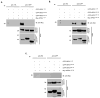
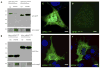
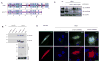
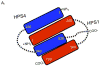
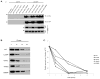
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS) is a group of rare autosomal recessive disorders characterized by oculocutaneous albinism, a bleeding tendency, and sporadic pulmonary fibrosis, granulomatous colitis or infections. Nine HPS-causing genes have been identified in humans. HPS-1 is the most severe subtype with a prevalence of ~1/1800 in northwest Puerto Rico due to a founder mutation in the HPS1 gene. Mutations in HPS genes affect the biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles such as melanosomes in melanocytes and platelet dense granules VSports手机版. Two of these genes (HPS1 and HPS4) encode the HPS1 and HPS4 proteins, which assemble to form a complex known as Biogenesis of Lysosome-related Organelle Complex 3 (BLOC-3). We report the identification of the interacting regions in HPS1 and HPS4 required for the formation of this complex. Two regions in HPS1, spanning amino acids 1-249 and 506-700 are required for binding to HPS4; the middle portion of HPS1 (residues 250-505) is not required for this interaction. Further interaction studies showed that the N-termini of HPS1 and HPS4 interact with each other and that a discrete region of HPS4 (residues 340-528) interacts with both the N- and C-termini of the HPS1 protein. Several missense mutations found in HPS-1 patients did not affect interaction with HPS4, but some mutations involving regions interacting with HPS4 caused instability of HPS1. These observations extend our understanding of BLOC-3 assembly and represent an important first step in the identification of domains responsible for the biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles. .
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B V体育安卓版. V. All rights reserved. .
Figures
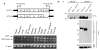
References
-
- Hermansky F, Pudlak P. Albinism associated with hemorrhagic diathesis and unusual pigmented reticular cells in the bone marrow: report of two cases with histochemical studies. Blood. 1959;14:162–169. - PubMed
-
- Schinella RA, Greco MA, Cobert BL, Denmark LW, Cox RP. Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome with granulomatous colitis. Ann Intern Med. 1980;9:220–23. - PubMed
-
- Gahl WA, Brantly M, Kaiser-Kupfer MI, Iwata F, Hazelwood S, Shotelersuk V, Duffy LF, Kuehl EM, Troendle J, Bernardini I. Genetic defect and clinical characteristics of patients with a form of oculocutaneous albinism (Hermansky- Pudlak syndrome) N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1258–1264. - "VSports手机版" PubMed
-
- Brantly M, Avila NA, Shotelersuk V, Lucero C, Huizing M, Gahl WA. Pulmonary function and high-resolution CT finding in patients with an inherited form of pulmonary fibrosis, Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, due to mutations in HPS-1. Chest. 2000;117:129–136. - PubMed (VSports)
-
- Oh J, Bailin T, Fukai K, Feng GH, Ho L, Mao JI, Frenk E, Tamura N, Spritz RA. Positional cloning of a gene for Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, a disorder of cytoplasmic organelles. Nat Genet. 1996;14:300–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
Substances
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
Grants and funding
"V体育官网入口" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
"V体育平台登录" Medical
Research Materials

