Immune reconstitution after anti-thymocyte globulin-conditioned hematopoietic cell transplantation
- PMID: 22985195
- PMCID: PMC3681879
- DOI: 10.3109/14653249.2012.715243
Immune reconstitution after anti-thymocyte globulin-conditioned hematopoietic cell transplantation
Abstract
Background aims: Anti-thymocyte globulin (ATG) is being used increasingly to prevent graft-versus-host disease (GvHD); however, its impact on immune reconstitution is relatively unknown. We (i) studied immune reconstitution after ATG-conditioned hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT), (ii) determined the factors influencing the reconstitution, and (iii) compared it with non-ATG-conditioned HCT VSports手机版. .
Methods: Immune cell subset counts were determined at 1-24 months post-transplant in 125 HCT recipients who received ATG during conditioning V体育安卓版. Subset counts were also determined in 46 non-ATG-conditioned patients (similarly treated). .
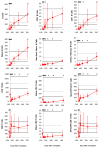
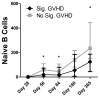
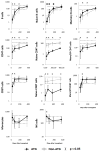
Results: (i) Reconstitution after ATG-conditioned HCT was fast for innate immune cells, intermediate for B cells and CD8 T cells, and very slow for CD4 T cells and invariant natural killer T (iNKT) (iNKT) cells V体育ios版. (ii) Faster reconstitution after ATG-conditioned HCT was associated with a higher number of cells of the same subset transferred with the graft in the case of memory B cells, naive CD4 T cells, naive CD8 T cells, iNKT cells and myeloid dendritic cells; lower recipient age in the case of naive CD4 T cells and naive CD8 T cells; cytomegalovirus recipient seropositivity in the case of memory/effector T cells; an absence of GvHD in the case of naive B cells; lower ATG serum levels in the case of most T-cell subsets, including iNKT cells; and higher ATG levels in the case of NK cells and B cells. (iii) Compared with non-ATG-conditioned HCT, reconstitution after ATG-conditioned HCT was slower for CD4 T cells, and faster for NK cells and B cells. .
Conclusions: ATG worsens the reconstitution of CD4 T cells but improves the reconstitution of NK and B cells VSports最新版本. .
"VSports app下载" Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Interest: J. S. has received a grant from Genzyme, Otherwise the authors declare no competing financial interests V体育平台登录.
Figures


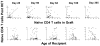
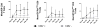
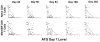
References
-
- Bosch M, Khan FM, Storek J. Immune reconstitution after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Curr Opin Hematol. 2012 Epub 2012/04/21. - PubMed
-
- Mackall C, Fry T, Gress R, Peggs K, Storek J, Toubert A. Background to hematopoietic cell transplantation, including post transplant immune recovery. Bone marrow transplantation. 2009;44(8):457–62. Epub 2009/10/29. - PubMed
-
- Seggewiss R, Einsele H. Immune reconstitution after allogeneic transplantation and expanding options for immunomodulation: an update. Blood. 2010;115(19):3861–8. Epub 2010/03/11. - PubMed
-
- Parkman R, Cohen G, Carter SL, Weinberg KI, Masinsin B, Guinan E, et al. Successful immune reconstitution decreases leukemic relapse and improves survival in recipients of unrelated cord blood transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2006;12(9):919–27. Epub 2006/08/22. - PubMed
-
- Hoegh-Petersen M, Sy S, Ugarte-Torres A, Williamson TS, Eliasziw M, Mansoor A, et al. High Epstein-Barr virus-specific T-cell counts are associated with near-zero likelihood of acute myeloid leukemia relapse after hematopoietic cell transplantation. Leukemia. 2012;26(2):359–62. Epub 2011/07/30. - PubMed
Publication types (VSports注册入口)
MeSH terms
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
Substances
VSports app下载 - Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
"VSports在线直播" Research Materials

