Signaling mechanisms regulating adult neural stem cells and neurogenesis
- PMID: 22982587
- PMCID: VSports手机版 - PMC3541438
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.09.002 (VSports app下载)
Signaling mechanisms regulating adult neural stem cells and neurogenesis
Abstract
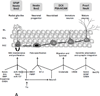
Background: Adult neurogenesis occurs throughout life in discrete regions of the mammalian brain and is tightly regulated via both extrinsic environmental influences and intrinsic genetic factors VSports手机版. In recent years, several crucial signaling pathways have been identified in regulating self-renewal, proliferation, and differentiation of neural stem cells, as well as migration and functional integration of developing neurons in the adult brain. .
Scope of review: Here we review our current understanding of signaling mechanisms, including Wnt, notch, sonic hedgehog, growth and neurotrophic factors, bone morphogenetic proteins, neurotransmitters, transcription factors, and epigenetic modulators, and crosstalk between these signaling pathways in the regulation of adult neurogenesis. We also highlight emerging principles in the vastly growing field of adult neural stem cell biology and neural plasticity V体育安卓版. .
Major conclusions: Recent methodological advances have enabled the field to identify signaling mechanisms that fine-tune and coordinate neurogenesis in the adult brain, leading to a better characterization of both cell-intrinsic and environmental cues defining the neurogenic niche. Significant questions related to niche cell identity and underlying regulatory mechanisms remain to be fully addressed and will be the focus of future studies. V体育ios版.
General significance: A full understanding of the role and function of individual signaling pathways in regulating neural stem cells and generation and integration of newborn neurons in the adult brain may lead to targeted new therapies for neurological diseases in humans. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled Biochemistry of Stem Cells. VSports最新版本.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B. V. All rights reserved V体育平台登录. .
Figures

References (V体育ios版)
-
- Gage FH. Mammalian neural stem cells. Science. 2000;287:1433–1438. - PubMed
-
- Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Bjork-Eriksson T, Alborn AM, Nordborg C, Peterson DA, Gage FH. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat. Med. 1998;4:1313–1317. - PubMed
-
- Roy NS, Wang S, Jiang L, Kang J, Benraiss A, Harrison-Restelli C, Fraser RA, Couldwell WT, Kawaguchi A, Okano H, Nedergaard M, Goldman SA. In vitro neurogenesis by progenitor cells isolated from the adult human hippocampus. Nat. Med. 2000;6:271–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
Grants and funding
"V体育2025版" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical (V体育平台登录)
VSports在线直播 - Research Materials

