HOXA9 promotes ovarian cancer growth by stimulating cancer-associated fibroblasts
- PMID: 22945634
- PMCID: PMC3461910
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI62229
HOXA9 promotes ovarian cancer growth by stimulating cancer-associated fibroblasts (VSports手机版)
Abstract (V体育平台登录)
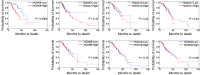
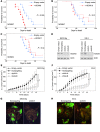
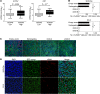
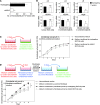
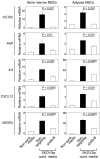
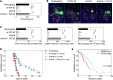
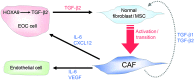
Epithelial ovarian cancers (EOCs) often exhibit morphologic features of embryonic Müllerian duct-derived tissue lineages and colonize peritoneal surfaces that overlie connective and adipose tissues. However, the mechanisms that enable EOC cells to readily adapt to the peritoneal environment are poorly understood. In this study, we show that expression of HOXA9, a Müllerian-patterning gene, is strongly associated with poor outcomes in patients with EOC and in mouse xenograft models of EOC. Whereas HOXA9 promoted EOC growth in vivo, HOXA9 did not stimulate autonomous tumor cell growth in vitro. On the other hand, expression of HOXA9 in EOC cells induced normal peritoneal fibroblasts to express markers of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and to stimulate growth of EOC and endothelial cells. Similarly, expression of HOXA9 in EOC cells induced normal adipose- and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to acquire features of CAFs VSports手机版. These effects of HOXA9 were due in substantial part to its transcriptional activation of the gene encoding TGF-β2 that acted in a paracrine manner on peritoneal fibroblasts and MSCs to induce CXCL12, IL-6, and VEGF-A expression. These results indicate that HOXA9 expression in EOC cells promotes a microenvironment that is permissive for tumor growth. .
Figures



References
-
- Naora H, Montell DJ. Ovarian cancer metastasis: Integrating insights from disparate model organisms. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(5):355–366. doi: 10.1038/nrc1611. - "VSports" DOI - PubMed
-
- Clements PB, Young RH. Atlas of Gynecologic Surgical Pathology. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA: WB Saunders; 2000.
-
- Pearson JC, Lemons D, McGinnis W. Modulating HOX gene functions during animal body patterning. . Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6(12):893–904. - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
Substances (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
V体育官网 - Molecular Biology Databases

