The role of bile after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in promoting weight loss and improving glycaemic control
- PMID: 22673227
- PMCID: PMC3404349
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2011-2145
"V体育安卓版" The role of bile after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in promoting weight loss and improving glycaemic control
Abstract
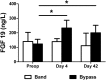
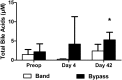
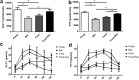
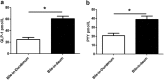
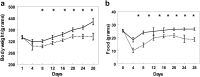
Gastric bypass leads to the remission of type 2 diabetes independently of weight loss. Our hypothesis is that changes in bile flow due to the altered anatomy may partly explain the metabolic outcomes of the operation. We prospectively studied 12 patients undergoing gastric bypass and six patients undergoing gastric banding over a 6-wk period. Plasma fibroblast growth factor (FGF)19, stimulated by bile acid absorption in the terminal ileum, and plasma bile acids were measured. In canine and rodent models, we investigated changes in the gut hormone response after altered bile flow. FGF19 and total plasma bile acids levels increased after gastric bypass compared with no change after gastric banding. In the canine model, both food and bile, on their own, stimulated satiety gut hormone responses. However, when combined, the response was doubled. In rats, drainage of endogenous bile into the terminal ileum was associated with an enhanced satiety gut hormone response, reduced food intake, and lower body weight. In conclusion, after gastric bypass, bile flow is altered, leading to increased plasma bile acids, FGF19, incretin. and satiety gut hormone concentrations. Elucidating the mechanism of action of gastric bypass surgery may lead to novel treatments for type 2 diabetes. VSports手机版.
Figures
References
-
- Claudel T, Staels B, Kuipers F. 2005. The farnesoid X receptor: a molecular link between bile acid and lipid and glucose metabolism. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:2020–2030 - PubMed
-
- Garg A, Grundy SM. 1994. Cholestyramine therapy for dyslipidemia in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. A short-term, double-blind, crossover trial. Ann Intern Med 121:416–422 - PubMed
-
- Fonseca VA, Rosenstock J, Wang AC, Truitt KE, Jones MR. 2008. Colesevelam HCl improves glycemic control and reduces LDL cholesterol in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes on sulfonylurea-based therapy. Diabetes Care 31:1479–1484 - V体育平台登录 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goldberg RB, Fonseca VA, Truitt KE, Jones MR. 2008. Efficacy and safety of colesevelam in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and inadequate glycemic control receiving insulin-based therapy. Arch Intern Med 168:1531–1540 - PubMed
-
- Bays HE, Goldberg RB, Truitt KE, Jones MR. 2008. Colesevelam hydrochloride therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with metformin: glucose and lipid effects. Arch Intern Med 168:1975–1983 - PubMed
Publication types
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
MeSH terms (VSports手机版)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
Substances
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
V体育官网 - Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
VSports手机版 - Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

