"VSports注册入口" Quantification of the relative roles of niche and neutral processes in structuring gastrointestinal microbiomes
- PMID: 22615407
- PMCID: PMC3382495
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1206721109
VSports注册入口 - Quantification of the relative roles of niche and neutral processes in structuring gastrointestinal microbiomes
Abstract
The theoretical description of the forces that shape ecological communities focuses around two classes of models. In niche theory, deterministic interactions between species, individuals, and the environment are considered the dominant factor, whereas in neutral theory, stochastic forces, such as demographic noise, speciation, and immigration, are dominant. Species abundance distributions predicted by the two classes of theory are difficult to distinguish empirically, making it problematic to deduce ecological dynamics from typical measures of diversity and community structure. Here, we show that the fusion of species abundance data with genome-derived measures of evolutionary distance can provide a clear indication of ecological dynamics, capable of quantifying the relative roles played by niche and neutral forces. We apply this technique to six gastrointestinal microbiomes drawn from three different domesticated vertebrates, using high-resolution surveys of microbial species abundance obtained from carefully curated deep 16S rRNA hypervariable tag sequencing data. Although the species abundance patterns are seemingly well fit by the neutral theory of metacommunity assembly, we show that this theory cannot account for the evolutionary patterns in the genomic data; moreover, our analyses strongly suggest that these microbiomes have, in fact, been assembled through processes that involve a significant nonneutral (niche) contribution. Our results demonstrate that high-resolution genomics can remove the ambiguities of process inference inherent in classic ecological measures and permits quantification of the forces shaping complex microbial communities VSports手机版. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
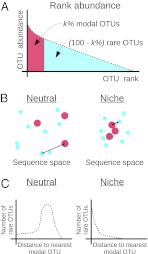
 of OTUs are labeled modal, whereas the remaining OTUs are labeled rare. (B) Sketch of the neutral and niche evolution processes in sequence space. Light blue OTUs are rare, whereas red OTUs are modal. For the neutral process, the average distance of a rare OTU to its closest modal OTU is large (indicated by the arrow). For the niche process, this distance is much smaller because rare OTUs cluster about the modal OTUs that define the niches. (C) Sketch of the expected distributions of distance to the closest modal OTU. For the neutral process, this distribution is peaked around some nonzero distance, which is close to the average distance between the OTUs in the dataset. In the niche process, the distribution monotonically decays with distance because the rare OTUs are attracted to the niches.
of OTUs are labeled modal, whereas the remaining OTUs are labeled rare. (B) Sketch of the neutral and niche evolution processes in sequence space. Light blue OTUs are rare, whereas red OTUs are modal. For the neutral process, the average distance of a rare OTU to its closest modal OTU is large (indicated by the arrow). For the niche process, this distance is much smaller because rare OTUs cluster about the modal OTUs that define the niches. (C) Sketch of the expected distributions of distance to the closest modal OTU. For the neutral process, this distribution is peaked around some nonzero distance, which is close to the average distance between the OTUs in the dataset. In the niche process, the distribution monotonically decays with distance because the rare OTUs are attracted to the niches.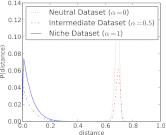
 shown for a fully niche-like model dataset
shown for a fully niche-like model dataset  , a fully neutral-like model dataset
, a fully neutral-like model dataset  , and an intermediate dataset
, and an intermediate dataset  . The results shown are the average of 5,000 Monte Carlo simulations for each dataset.
. The results shown are the average of 5,000 Monte Carlo simulations for each dataset.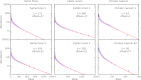
 of the model is fit to correspond to the exponential tail in rank abundance. Offset represents the number of high-abundance OTUs that do not fit the neutral model.
of the model is fit to correspond to the exponential tail in rank abundance. Offset represents the number of high-abundance OTUs that do not fit the neutral model.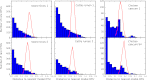
 (blue bars indicate experimental data). Red lines indicate the results of the metric applied to sequences that were randomized while preserving rank abundance and sequence statistics (main text). Cattle and swine datasets share the same y axis.
(blue bars indicate experimental data). Red lines indicate the results of the metric applied to sequences that were randomized while preserving rank abundance and sequence statistics (main text). Cattle and swine datasets share the same y axis.References (V体育官网)
-
- Tokeshi M. Species Coexistence: Ecological and Evolutionary Perspectives. New York: Wiley–Blackwell; 1999.
-
- Chesson P. Mechanisms of maintenance of species diversity. Annu Rev Ecol Syst. 2000;31:343–366.
-
- Hutchinson GE. Homage to Santa Rosalia, or why are there so many kinds of animals? Am Nat. 1959;93:145–159.
-
- Hutchinson GE. The paradox of the plankton. Am Nat. 1961;95:137–145.
-
- Chave J, Muller-Landau HC, Levin SA. Comparing classical community models: Theoretical consequences for patterns of diversity. Am Nat. 2002;159:1–23. - PubMed
Publication types
- VSports - Actions
MeSH terms
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
"VSports在线直播" Substances
V体育官网入口 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

