Caspases in synaptic plasticity
- PMID: 22583788
- PMCID: PMC3366905
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-6606-5-15
Caspases in synaptic plasticity (VSports)
Abstract
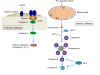
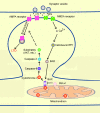
Caspases are a family of cysteine proteases that play key roles in programmed cell death (apoptosis) VSports手机版. Mounting evidence in recent years shows that caspases also have important non-apoptotic functions in multiple cellular processes, such as synaptic plasticity, dendritic development, learning and memory. In this article, we review the studies on the non-apoptotic functions of caspases in neurons, with a focus on their roles in synaptic plasticity, learning and memory and neurodegeneration. .
Figures
References (VSports在线直播)
-
- Li J, Yuan J. Caspases in apoptosis and beyond. Oncogene. 2008;27:6194–6206. - VSports最新版本 - PubMed
-
- Yuan J, Shaham S, Ledoux S, Ellis HM, Horvitz HR. The C. elegans cell death gene ced-3 encodes a protein similar to mammalian interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. Cell. 1993;75:641–652. - PubMed
-
- Ellis HM, Horvitz HR. Genetic control of programmed cell death in the nematode C. elegans. Cell. 1986;44:817–829. - PubMed
-
- Lavrik I, Golks A, Krammer PH. Death receptor signaling. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:265–267. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Du F, Wang X. TNF-alpha induces two distinct caspase-8 activation pathways. Cell. 2008;133:693–703. - PubMed
VSports app下载 - Publication types
MeSH terms
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
Substances
VSports - LinkOut - more resources
V体育2025版 - Full Text Sources

