Induction of the neural crest state: control of stem cell attributes by gene regulatory, post-transcriptional and epigenetic interactions
- PMID: 22583479
- PMCID: PMC3354335
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.03.014
Induction of the neural crest state: control of stem cell attributes by gene regulatory, post-transcriptional and epigenetic interactions (VSports手机版)
Abstract (VSports手机版)
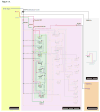
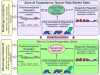
Neural crest cells are a population of multipotent stem cell-like progenitors that arise at the neural plate border in vertebrates, migrate extensively, and give rise to diverse derivatives such as melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage and bone, smooth muscle, peripheral and enteric neurons and glia. The neural crest gene regulatory network (NC-GRN) includes a number of key factors that are used reiteratively to control multiple steps in the development of neural crest cells, including the acquisition of stem cell attributes VSports手机版. It is therefore essential to understand the mechanisms that control the distinct functions of such reiteratively used factors in different cellular contexts. The context-dependent control of neural crest specification is achieved through combinatorial interaction with other factors, post-transcriptional and post-translational modifications, and the epigenetic status and chromatin state of target genes. Here we review the current understanding of the NC-GRN, including the role of the neural crest specifiers, their links to the control of "stemness," and their dynamic context-dependent regulation during the formation of neural crest progenitors. .
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved V体育安卓版. .
Figures

References
-
- Acloque H, Ocana OH, Matheu A, Rizzoti K, Wise C, Lovell-Badge R, Nieto MA. Reciprocal repression between Sox3 and snail transcription factors defines embryonic territories at gastrulation. Dev Cell. 2011;21:546–558. - "VSports最新版本" PMC - PubMed
-
- Aday AW, Zhu LJ, Lakshmanan A, Wang J, Lawson ND. Identification of cis regulatory features in the embryonic zebrafish genome through large-scale profiling of H3K4me1 and H3K4me3 binding sites. Dev Biol. 2011;357:450–462. - "VSports" PMC - PubMed
-
- Akiyama H, Chaboissier MC, Martin JF, Schedl A, de Crombrugghe B. The transcription factor Sox9 has essential roles in successive steps of the chondrocyte differentiation pathway and is required for expression of Sox5 and Sox6. Genes Dev. 2002;16:2813–2828. - V体育官网 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alves CC, Carneiro F, Hoefler H, Becker KF. Role of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulator Slug in primary human cancers. Front Biosci. 2009;14:3035–3050. - VSports最新版本 - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
MeSH terms
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

