"V体育官网" T cell factor-1 and β-catenin control the development of memory-like CD8 thymocytes
- PMID: 22492686
- PMCID: PMC3471543 (VSports app下载)
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103729
T cell factor-1 and β-catenin control the development of memory-like CD8 thymocytes (V体育安卓版)
Abstract
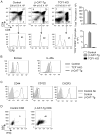
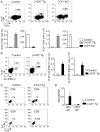
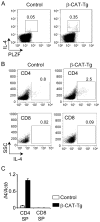
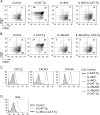
Innate memory-like CD8 thymocytes develop and acquire effector function during maturation in the absence of encounter with Ags. In this study, we demonstrate that enhanced function of transcription factors T cell factor (TCF)-1 and β-catenin regulate the frequency of promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger (PLZF)-expressing, IL-4-producing thymocytes that promote the generation of eomesodermin-expressing memory-like CD8 thymocytes in trans VSports手机版. In contrast, TCF1-deficient mice do not have PLZF-expressing thymocytes and eomesodermin-expressing memory-like CD8 thymocytes. Generation of TCF1 and β-catenin-dependent memory-like CD8 thymocytes is non-cell-intrinsic and requires the expression of IL-4 and IL-4R. CD8 memory-like thymocytes migrate to the peripheral lymphoid organs, and the memory-like CD8 T cells rapidly produce IFN-γ. Thus, TCF1 and β-catenin regulate the generation of PLZF-expressing thymocytes and thereby facilitate the generation of memory-like CD8 T cells in the thymus. .
Figures
References
-
- Lee YJ, Jameson SC, Hogquist KA. Alternative memory in the CD8 T cell lineage. Trends Immunol. 2011;32:50–56. - PMC (VSports手机版) - PubMed
-
- Broussard C, Fleischacker C, Horai R, Chetana M, Venegas AM, Sharp LL, Hedrick SM, Fowlkes BJ, Schwartzberg PL. Altered development of CD8+ T cell lineages in mice deficient for the Tec kinases Itk and Rlk. Immunity. 2006;25:93–104. - PubMed
-
- Atherly LO, Lucas JA, Felices M, Yin CC, Reiner SL, Berg LJ. The Tec family tyrosine kinases Itk and Rlk regulate the development of conventional CD8+ T cells. Immunity. 2006;25:79–91. - PubMed
-
- Jordan MS, Smith JE, Burns JC, Austin JE, Nichols KE, Aschenbrenner AC, Koretzky GA. Complementation in trans of altered thymocyte development in mice expressing mutant forms of the adaptor molecule SLP76. Immunity. 2008;28:359–369. - "VSports app下载" PMC - PubMed
-
- Prince AL, Yin CC, Enos ME, Felices M, Berg LJ. The Tec kinases Itk and Rlk regulate conventional versus innate T-cell development. Immunol Rev. 2009;228:115–131. - V体育官网 - PMC - PubMed
VSports注册入口 - Publication types
MeSH terms
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- VSports app下载 - Actions
"VSports在线直播" Substances
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
Grants and funding
V体育平台登录 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials (VSports app下载)

