MicroRNAs: Processing, Maturation, Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions
- PMID: 22468167
- PMCID: V体育ios版 - PMC3315687
MicroRNAs: Processing, Maturation, Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions
Abstract
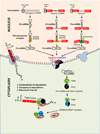
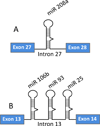
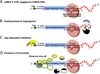
The remarkable discovery of small noncoding microRNAs (miRNAs) and their role in posttranscriptional gene regulation have revealed another fine-tuning step in the expression of genetic information VSports手机版. A large number of cellular pathways, which act in organismal development and are important in health and disease, appear to be modulated by miRNAs. At the molecular level, miRNAs restrain the production of proteins by affecting the stability of their target mRNA and/or by down-regulating their translation. This review attempts to offer a snapshot of aspects of miRNA coding, processing, target recognition and function in animals. Our goal here is to provide the readers with a thought-provoking and mechanistic introduction to the miRNA world rather than with a detailed encyclopedia. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. TheC elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. - VSports最新版本 - PubMed
-
- Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M, et al. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2000;403:901–906. - PubMed (VSports最新版本)
-
- Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T. Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science. 2001;294:853–858. - PubMed
-
- Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP. An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2001;294:858–862. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Ambros V. An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2001;294:862–864. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
