Liver hyperplasia after tamoxifen induction of Myc in a transgenic medaka model
- PMID: 22422827
- PMCID: "V体育官网" PMC3380712
- DOI: V体育ios版 - 10.1242/dmm.008730
Liver hyperplasia after tamoxifen induction of Myc in a transgenic medaka model
Abstract
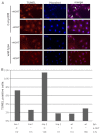
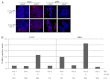
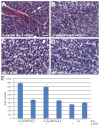
Myc is a global transcriptional regulator and one of the most frequently overexpressed oncoproteins in human tumors. It is well established that activation of Myc leads to enhanced cell proliferation but can also lead to increased apoptosis VSports手机版. The use of animal models expressing deregulated levels of Myc has helped to both elucidate its function in normal cells and give insight into how Myc initiates and maintains tumorigenesis. Analyses of the medaka (Oryzias latipes) genome uncovered the unexpected presence of two Myc gene copies in this teleost species. Comparison of these Myc versions to other vertebrate species revealed that one gene, myc17, differs by the loss of some conserved regulatory protein motifs present in all other known Myc genes. To investigate how such differences might affect the basic biological functions of Myc, we generated a tamoxifen-inducible in vivo model utilizing a natural, fish-specific Myc gene. Using this model we show that, when activated, Myc17 leads to increased proliferation and to apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner, similar to human Myc. We have also shown that long-term Myc17 activation triggers liver hyperplasia in adult fish, allowing this newly established transgenic medaka model to be used to study the transition from hyperplasia to liver cancer and to identify Myc-induced tumorigenesis modifiers. .
"VSports手机版" Figures
References
-
- Adhikary S., Eilers M. (2005). Transcriptional regulation and transformation by Myc proteins. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 635–645 - "V体育官网" PubMed
-
- Amati B., Frank S. R., Donjerkovic D., Taubert S. (2001). Function of the c-Myc oncoprotein in chromatin remodeling and transcription. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1471, 135–145 - PubMed
-
- Bhatia K., Huppi K., Spangler G., Siwarski D., Iyer R., Magrath I. (1993). Point mutations in the c-Myc transactivation domain are common in Burkitt’s lymphoma and mouse plasmacytomas. Nat. Genet. 5, 56–61 - PubMed (VSports)
-
- Blyth K., Terry A., O’Hara M., Baxter E. W., Campbell M., Stewart M., Donehower L. A., Onions D. E., Neil J. C., Cameron E. R. (1995). Synergy between a human c-myc transgene and p53 null genotype in murine thymic lymphomas: contrasting effects of homozygous and heterozygous p53 loss. Oncogene 10, 1717–1723 - PubMed
-
- Blyth K., Stewart M., Bell M., James C., Evan G., Neil J. C., Cameron E. R. (2000). Sensitivity to myc-induced apoptosis is retained in spontaneous and transplanted lymphomas of CD2-mycER mice. Oncogene 19, 773–782 - PubMed
Publication types
- "VSports" Actions
MeSH terms
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
"VSports在线直播" Substances
- "V体育官网" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions

