Development and function of invariant natural killer T cells producing T(h)2- and T(h)17-cytokines
- PMID: 22346732
- PMCID: PMC3274505
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001255
"VSports注册入口" Development and function of invariant natural killer T cells producing T(h)2- and T(h)17-cytokines
"VSports app下载" Abstract
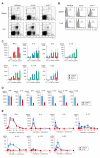
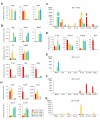
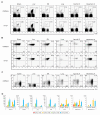
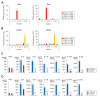
There is heterogeneity in invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells based on the expression of CD4 and the IL-17 receptor B (IL-17RB), a receptor for IL-25 which is a key factor in T(H)2 immunity. However, the development pathway and precise function of these iNKT cell subtypes remain unknown. IL-17RB⁺iNKT cells are present in the thymic CD44⁺/⁻ NK1 VSports手机版. 1⁻ population and develop normally even in the absence of IL-15, which is required for maturation and homeostasis of IL-17RB⁻iNKT cells producing IFN-γ. These results suggest that iNKT cells contain at least two subtypes, IL-17RB⁺ and IL-17RB⁻ subsets. The IL-17RB⁺iNKT subtypes can be further divided into two subtypes on the basis of CD4 expression both in the thymus and in the periphery. CD4⁺ IL-17RB⁺iNKT cells produce T(H)2 (IL-13), T(H)9 (IL-9 and IL-10), and T(H)17 (IL-17A and IL-22) cytokines in response to IL-25 in an E4BP4-dependent fashion, whereas CD4⁻ IL-17RB⁺iNKT cells are a retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor (ROR)γt⁺ subset producing T(H)17 cytokines upon stimulation with IL-23 in an E4BP4-independent fashion. These IL-17RB⁺iNKT cell subtypes are abundantly present in the lung in the steady state and mediate the pathogenesis in virus-induced airway hyperreactivity (AHR). In this study we demonstrated that the IL-17RB⁺iNKT cell subsets develop distinct from classical iNKT cell developmental stages in the thymus and play important roles in the pathogenesis of airway diseases. .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Taniguchi M, Harada M, Kojo S, Nakayama T, Wakao H. The regulatory role of Valpha14 NKT cells in innate and acquired immune response. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:483–513. - PubMed
-
- Lantz O, Bendelac A. An invariant T cell receptor alpha chain is used by a unique subset of major histocompatibility complex class I-specific CD4+ and CD4−8− T cells in mice and humans. J Exp Med. 1994;180:1097–1106. - "V体育平台登录" PMC - PubMed
-
- Bendelac A, Lantz O, Quimby M. E, Yewdell J. W, Bennink J. R, et al. CD1 recognition by mouse NK1+ T lymphocytes. Science. 1995;268:863–865. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
Substances
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
VSports最新版本 - LinkOut - more resources
"VSports注册入口" Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials (VSports)
Miscellaneous

