Roles of STAT3 and ZEB1 proteins in E-cadherin down-regulation and human colorectal cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- PMID: 22205702
- PMCID: PMC3285352
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.295964
Roles of STAT3 and ZEB1 proteins in E-cadherin down-regulation and human colorectal cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition
Abstract
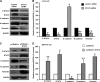
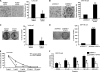
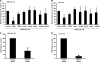
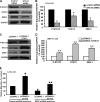
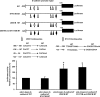
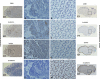
The progression of colorectal carcinoma (CRC) to invasive and metastatic disease may involve localized occurrences of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). However, mechanisms of the EMT process in CRC progression are not fully understood. We previously showed that knockdown of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) up-regulated E-cadherin (a key component in EMT progression) in CRC. In this study, we examined the roles of STAT3 in CRC EMT and ZEB1, an EMT inducer, in STAT3-induced down-regulation of E-cadherin. Knockdown of STAT3 significantly increased E-cadherin and decreased N-cadherin and vimentin expressions in highly invasive LoVo CRC cells. Meanwhile, overexpression of STAT3 significantly reduced E-cadherin and enhanced N-cadherin and vimentin expressions in weakly invasive SW1116 CRC cells. Activation of STAT3 significantly increased CRC cell invasiveness and resistance to apoptosis. Knockdown of STAT3 dramatically enhanced chemosensitivity of CRC cells to fluorouracil. STAT3 regulated ZEB1 expression in CRC cells, and the STAT3-induced decrease in E-cadherin and cell invasion depended on activation of ZEB1 in CRC cells. Additionally, pSTAT3(Tyr-705) and ZEB1 expressions were significantly correlated with TNM (tumor, lymph node, and metastasis stages) (p < 0 VSports手机版. 01). In conclusion, STAT3 may directly mediate EMT progression and regulate ZEB1 expression in CRC. ZEB1 may participate in STAT3-induced cell invasion and E-cadherin down-regulation in CRC cells. The expressions of pSTAT3(Tyr-705) and ZEB1 may be positively associated with CRC metastasis. Our data may provide potential targets to prevent and/or treat CRC invasion and metastasis. .
Figures

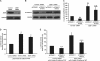

"VSports" References
-
- Bates R. C., Mercurio A. M. (2005) The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and colorectal cancer progression. Cancer Biol. Ther. 4, 365–370 - PubMed
-
- Markowitz S. D., Dawson D. M., Willis J., Willson J. K. (2002) Focus on colon cancer. Cancer Cell 1, 233–236 - PubMed
-
- Thiery J. P., Acloque H., Huang R. Y., Nieto M. A. (2009) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 139, 871–890 - V体育2025版 - PubMed
-
- Hay E. D. (1995) An overview of epithelio-mesenchymal transformation. Acta Anat. 154, 8–20 - PubMed
-
- Savagner P. (2001) Leaving the neighborhood. Molecular mechanisms involved during epithelial-mesenchymal transition. BioEssays 23, 912–923 - PubMed
Publication types
- V体育2025版 - Actions
"V体育ios版" MeSH terms
- V体育官网 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
Substances
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
VSports - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

