VSports最新版本 - Reducing the effects of PCR amplification and sequencing artifacts on 16S rRNA-based studies
- PMID: 22194782
- PMCID: PMC3237409
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027310
Reducing the effects of PCR amplification and sequencing artifacts on 16S rRNA-based studies
"V体育官网入口" Abstract
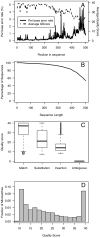
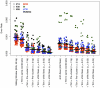
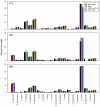
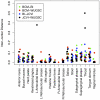
The advent of next generation sequencing has coincided with a growth in interest in using these approaches to better understand the role of the structure and function of the microbial communities in human, animal, and environmental health. Yet, use of next generation sequencing to perform 16S rRNA gene sequence surveys has resulted in considerable controversy surrounding the effects of sequencing errors on downstream analyses. We analyzed 2. 7×10(6) reads distributed among 90 identical mock community samples, which were collections of genomic DNA from 21 different species with known 16S rRNA gene sequences; we observed an average error rate of 0. 0060. To improve this error rate, we evaluated numerous methods of identifying bad sequence reads, identifying regions within reads of poor quality, and correcting base calls and were able to reduce the overall error rate to 0. 0002. Implementation of the PyroNoise algorithm provided the best combination of error rate, sequence length, and number of sequences. Perhaps more problematic than sequencing errors was the presence of chimeras generated during PCR. Because we knew the true sequences within the mock community and the chimeras they could form, we identified 8% of the raw sequence reads as chimeric. After quality filtering the raw sequences and using the Uchime chimera detection program, the overall chimera rate decreased to 1%. The chimeras that could not be detected were largely responsible for the identification of spurious operational taxonomic units (OTUs) and genus-level phylotypes. The number of spurious OTUs and phylotypes increased with sequencing effort indicating that comparison of communities should be made using an equal number of sequences. Finally, we applied our improved quality-filtering pipeline to several benchmarking studies and observed that even with our stringent data curation pipeline, biases in the data generation pipeline and batch effects were observed that could potentially confound the interpretation of microbial community data VSports手机版. .
"V体育平台登录" Conflict of interest statement
"VSports最新版本" Figures



References (V体育官网)
-
- Pace NR, Stahl DA, Lane DJ, Olsen GJ. Analyzing natural microbial populations by rRNA sequences. ASM News. 1985;51:4–12.
-
- Huber JA, Mark Welch DB, Morrison HG, Huse SM, Neal PR, et al. Microbial population structures in the deep marine biosphere. Science. 2007;318:97–100. - PubMed
-
- Prosser JI. Replicate or lie. Environ Microbiol. 2010;12:1806–1810. - V体育官网入口 - PubMed
-
- Relman DA, Schmidt TM, MacDermott RP, Falkow S. Identification of the uncultured bacillus of Whipple's disease. N Engl J Med. 1992;327:293–301. - PubMed
Publication types
"V体育官网入口" MeSH terms
- VSports手机版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
Substances
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
"V体育官网入口" Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

