Mouse resistin modulates adipogenesis and glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes through the ROR1 receptor
- PMID: 22074948
- PMCID: VSports在线直播 - PMC5417166
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2011-1027
VSports app下载 - Mouse resistin modulates adipogenesis and glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes through the ROR1 receptor
Abstract
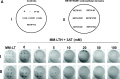
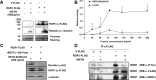
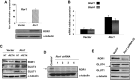
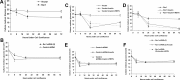
Mouse resistin, a cysteine-rich protein primarily secreted from mature adipocytes, is involved in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Human resistin, however, is mainly secreted by immune mononuclear cells, and it competes with lipopolysaccharide for the binding to Toll-like receptor 4, which could mediate some of the well-known proinflammatory effects of resistin in humans. In addition, resistin has been involved in the regulation of many cell differentiation and proliferation processes, suggesting that different receptors could be involved in mediating its numerous effects. Thus, a recent work identifies an isoform of Decorin (Δ Decorin) as a functional resistin receptor in adipocyte progenitors that may regulate white adipose tissue expansion. Our work shows that the mouse receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor (ROR)1 could mediate some of the described functions of resistin in 3T3-L1 adipogenesis and glucose uptake VSports手机版. We have demonstrated an interaction of mouse resistin with specific domains of the extracellular region of the ROR1 receptor. This interaction results in the inhibition of ROR1 phosphorylation, modulates ERK1/2 phosphorylation, and regulates suppressor of cytokine signaling 3, glucose transporter 4, and glucose transporter 1 expression. Moreover, mouse resistin modulates glucose uptake and promotes adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells through ROR1. In summary, our results identify mouse resistin as a potential inhibitory ligand for the receptor ROR1 and demonstrate, for the first time, that ROR1 plays an important role in adipogenesis and glucose homeostasis in 3T3-L1 cells. These data open a new line of research that could explain important questions about the resistin mechanism of action in adipogenesis and in the development of insulin resistance. .
Figures (V体育官网入口)



References
-
- Galic S , Oakhill JS , Steinberg GR. 2010. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Mol Cell Endocrinol 316:129–139. - PubMed
-
- Steppan CM , Lazar MA. 2002. Resistin and obesity-associated insulin resistance. Trends Endocrinol Metab 13:18–23 - PubMed
-
- Steppan CM , Lazar MA. 2004. The current biology of resistin. J Intern Med 255:439–447 - PubMed
-
- Filková M , Haluzík M , Gay S , Senolt L. 2009. The role of resistin as a regulator of inflammation: implications for various human pathologies. Clin Immunol 133:157–170 - PubMed (V体育平台登录)
Publication types
- "VSports app下载" Actions
"V体育2025版" MeSH terms
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
Substances
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (VSports手机版)
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
"V体育安卓版" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

