Dynamic distribution of the SecA and SecY translocase subunits and septal localization of the HtrA surface chaperone/protease during Streptococcus pneumoniae D39 cell division
- PMID: 21990615
- PMCID: "VSports最新版本" PMC3188284
- DOI: VSports最新版本 - 10.1128/mBio.00202-11
"V体育官网入口" Dynamic distribution of the SecA and SecY translocase subunits and septal localization of the HtrA surface chaperone/protease during Streptococcus pneumoniae D39 cell division
Abstract (V体育ios版)
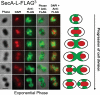
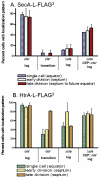
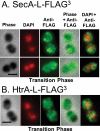
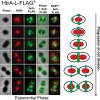
The Sec translocase pathway is the major route for protein transport across and into the cytoplasmic membrane of bacteria. Previous studies reported that the SecA translocase ATP-binding subunit and the cell surface HtrA protease/chaperone formed a single microdomain, termed "ExPortal," in some species of ellipsoidal (ovococcus) Gram-positive bacteria, including Streptococcus pyogenes. To investigate the generality of microdomain formation, we determined the distribution of SecA and SecY by immunofluorescent microscopy in Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), which is an ovococcus species evolutionarily distant from S. pyogenes. In the majority (≥ 75%) of exponentially growing cells, S. pneumoniae SecA (SecA (Spn)) and SecY (Spn) located dynamically in cells at different stages of division. In early divisional cells, both Sec subunits concentrated at equators, which are future sites of constriction. Further along in division, SecA(Spn) and SecY(Spn) remained localized at mid-cell septa. In late divisional cells, both Sec subunits were hemispherically distributed in the regions between septa and the future equators of dividing cells VSports手机版. In contrast, the HtrA (Spn) homologue localized to the equators and septa of most (> 90%) dividing cells, whereas the SrtA(Spn) sortase located over the surface of cells in no discernable pattern. This dynamic pattern of Sec distribution was not perturbed by the absence of flotillin family proteins, but was largely absent in most cells in early stationary phase and in cls mutants lacking cardiolipin synthase. These results do not support the existence of an ExPortal microdomain in S. pneumoniae. Instead, the localization of the pneumococcal Sec translocase depends on the stage of cell division and anionic phospholipid content. .
Importance: Two patterns of Sec translocase distribution, an ExPortal microdomain in certain ovococcus-shaped species like Streptococcus pyogenes and a spiral pattern in rod-shaped species like Bacillus subtilis, have been reported for Gram-positive bacteria. This study provides evidence for a third pattern of Sec localization in the ovococcus human pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae. The SecA motor and SecY channel subunits of the Sec translocase localize dynamically to different places in the mid-cell region during the division cycle of exponentially growing, but not stationary-phase, S. pneumoniae. Unexpectedly, the S. pneumoniae HtrA (HtrA(Spn)) protease/chaperone principally localizes to cell equators and division septa. The coincident localization of SecA(Spn), SecY (Spn), and HtrA (Spn) to regions of peptidoglycan (PG) biosynthesis in unstressed, growing cells suggests that the pneumococcal Sec translocase directs assembly of the PG biosynthesis apparatus to regions where it is needed during division and that HtrA(Spn) may play a general role in quality control of proteins exported by the Sec translocase V体育安卓版. .
VSports手机版 - Figures
References
-
- du Plessis DJ, Nouwen N, Driessen AJ. 2011. The Sec translocase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1808:851–865 - PubMed
-
- Sardis MF, Economou A. 2010. SecA: a tale of two protomers. Mol. Microbiol. 76:1070–1081 - "VSports最新版本" PubMed
-
- Gold VA, et al. 2010. The action of cardiolipin on the bacterial translocon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107:10044–10049 - "VSports注册入口" PMC - PubMed
-
- Campo N, et al. 2004. Subcellular sites for bacterial protein export. Mol. Microbiol. 53:1583–1599 - PubMed
-
- Rosch J, Caparon M. 2004. A microdomain for protein secretion in Gram-positive bacteria. Science 304:1513–1515 - PubMed
"V体育安卓版" Publication types
MeSH terms
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育2025版)
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
VSports最新版本 - Substances
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

