Assessment of 2q23.1 microdeletion syndrome implicates MBD5 as a single causal locus of intellectual disability, epilepsy, and autism spectrum disorder
- PMID: 21981781
- PMCID: PMC3188839
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.09.011
"VSports在线直播" Assessment of 2q23.1 microdeletion syndrome implicates MBD5 as a single causal locus of intellectual disability, epilepsy, and autism spectrum disorder
Abstract
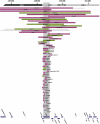
Persons with neurodevelopmental disorders or autism spectrum disorder (ASD) often harbor chromosomal microdeletions, yet the individual genetic contributors within these regions have not been systematically evaluated. We established a consortium of clinical diagnostic and research laboratories to accumulate a large cohort with genetic alterations of chromosomal region 2q23. 1 and acquired 65 subjects with microdeletion or translocation. We sequenced translocation breakpoints; aligned microdeletions to determine the critical region; assessed effects on mRNA expression; and examined medical records, photos, and clinical evaluations. We identified a single gene, methyl-CpG-binding domain 5 (MBD5), as the only locus that defined the critical region. Partial or complete deletion of MBD5 was associated with haploinsufficiency of mRNA expression, intellectual disability, epilepsy, and autistic features. Fourteen alterations, including partial deletions of noncoding regions not typically captured or considered pathogenic by current diagnostic screening, disrupted MBD5 alone. Expression profiles and clinical characteristics were largely indistinguishable between MBD5-specific alteration and deletion of the entire 2q23. 1 interval. No copy-number alterations of MBD5 were observed in 7878 controls, suggesting MBD5 alterations are highly penetrant. We surveyed MBD5 coding variations among 747 ASD subjects compared to 2043 non-ASD subjects analyzed by whole-exome sequencing and detected an association with a highly conserved methyl-CpG-binding domain missense variant, p. 79Gly>Glu (c VSports手机版. 236G>A) (p = 0. 012). These results suggest that genetic alterations of MBD5 cause features of 2q23. 1 microdeletion syndrome and that this epigenetic regulator significantly contributes to ASD risk, warranting further consideration in research and clinical diagnostic screening and highlighting the importance of chromatin remodeling in the etiology of these complex disorders. .
Copyright © 2011 The American Society of Human Genetics V体育安卓版. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. .
VSports手机版 - Figures


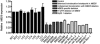
V体育ios版 - Comment in
-
Getting to the bottom of autism spectrum and related disorders: MBD5 as a key contributor.Clin Genet. 2012 Apr;81(4):363-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2011.01836.x. Epub 2012 Jan 16. Clin Genet. 2012. PMID: 22171639 No abstract available.
"V体育ios版" References
-
- Vissers L.E., de Vries B.B., Osoegawa K., Janssen I.M., Feuth T., Choy C.O., Straatman H., van der Vliet W., Huys E.H., van Rijk A. Array-based comparative genomic hybridization for the genomewide detection of submicroscopic chromosomal abnormalities. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003;73:1261–1270. - VSports手机版 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Williams S.R., Mullegama S.V., Rosenfeld J.A., Dagli A.I., Hatchwell E., Allen W.P., Williams C.A., Elsea S.H. Haploinsufficiency of MBD5 associated with a syndrome involving microcephaly, intellectual disabilities, severe speech impairment, and seizures. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2010;18:436–441. - PMC (V体育平台登录) - PubMed
-
- Wagenstaller J., Spranger S., Lorenz-Depiereux B., Kazmierczak B., Nathrath M., Wahl D., Heye B., Glaser D., Liebscher V., Meitinger T., Strom T.M. Copy-number variations measured by single-nucleotide-polymorphism oligonucleotide arrays in patients with mental retardation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007;81:768–779. - PMC (VSports最新版本) - PubMed
-
- Koolen D.A., Vissers L.E., Nillesen W., Smeets D., van Ravenswaaij C.M., Sistermans E.A., Veltman J.A., de Vries B.B. A novel microdeletion, del(2)(q22.3q23.3) in a mentally retarded patient, detected by array-based comparative genomic hybridization. Clin. Genet. 2004;65:429–432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- Actions (V体育ios版)
Substances
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
Grants and funding
- HD065286/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- GM061354/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL-102924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- "V体育安卓版" RC2 HL102924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32MH087123/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HL-102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-102923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 MH087123/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- "VSports注册入口" UC2 HL103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM061354/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- V体育官网入口 - UC2 HL102923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD065286/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
VSports最新版本 - Medical
Research Materials (VSports在线直播)

