Incidence and prevalence of copper deficiency following roux-en-y gastric bypass surgery
- PMID: 21876546
- PMCID: PMC3748601
- DOI: 10.1038/ijo.2011.159
Incidence and prevalence of copper deficiency following roux-en-y gastric bypass surgery
Abstract
Introduction and objectives: The frequency of copper deficiency and clinical manifestations following roux-en-y gastric bypass (RYGB) surgery is not yet clear VSports手机版. Objectives were to determine the prevalence and incidence of copper deficiency in patients who have undergone RYGB. .
Design and methods: We sought to determine the number of RYGB patients undergoing medical and nutritional follow-up visits at the Emory Bariatric Center who experienced copper deficiency and associated hematological and neurological complaints (n=136). Separately, in patients followed longitudinally before and during 6 and 24 months following RYGB surgery, we obtained measures of copper status (n=16) V体育安卓版. Systemic blood cell counts and measures of copper, zinc and ceruloplasmin were determined using standardized assays in reference laboratories including atomic absorption spectrometry and immunoassays. .
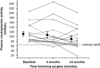
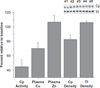
Results: Thirteen patients were identified to have copper deficiency suggesting a prevalence of copper deficiency of 9. 6%, and the majority of these had concomitant complications including anemia, leukopenia and various neuro-muscular abnormalities. In the longitudinal study, plasma copper concentrations and ceruloplasmin activity decreased over 6 and 24 months following surgery, respectively (P<0. 05), but plasma zinc concentrations did not change. A simultaneous decrease in white blood cells was observed (P<0 V体育ios版. 05). The incidence of copper deficiency in these subjects was determined to be 18. 8%. .
Conclusions: The prevalence and incidence of copper deficiency following RYGB surgery was determined to be 9. 6% and 18. 8%, respectively, with many patients experiencing mild-to-moderate symptoms. Given that copper deficiency can lead to serious and irreversible complications if untreated, frequent monitoring of the copper status of RYGB patients is warranted. VSports最新版本.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
V体育平台登录 - Figures

Comment in
-
Obesity: micronutrient deficiencies after RYGB surgery. (V体育安卓版)Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011 Sep 20;7(11):632. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2011.163. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21931367 No abstract available.
References
-
- Failla ML, Johnson MA, Prohaska JR. Copper. In: Bowman BA, Russell RM, editors. Present Knowledge in Nutrition. 8th ed. Washington, DC: ILSI Press; 2001. pp. 373–383.
-
- Andreini C, Banci L, Bertini I, Rosato A. Occurrence of copper proteins through the three domains of life: a bioinformatics approach. J Proteome Res. 2008;7:209–216. - PubMed
-
- Matoba S, Kang JG, Patino WD, Wragg A, Boehm M, Gavrilova O, et al. p53 regulates mitochondrial respiration. Science. 2006;312:1650–1653. - PubMed
Publication types (V体育ios版)
- "VSports" Actions
"V体育2025版" MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
"VSports app下载" Substances
V体育2025版 - Grants and funding
V体育安卓版 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
"VSports在线直播" Research Materials

