VSports手机版 - The dynamics of cortical and hippocampal atrophy in Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 21825241
- PMCID: "VSports手机版" PMC3248949
- DOI: 10.1001/archneurol.2011.167
The dynamics of cortical and hippocampal atrophy in Alzheimer disease
Abstract
Objective: To characterize rates of regional Alzheimer disease (AD)-specific brain atrophy across the presymptomatic, mild cognitive impairment, and dementia stages VSports手机版. .
Design: Multicenter case-control study of neuroimaging, cerebrospinal fluid, and cognitive test score data from the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. V体育安卓版.
Setting: Research centers across the United States and Canada. V体育ios版.
Patients: We examined a total of 317 participants with baseline cerebrospinal fluid biomarker measurements and 3 T1-weighted magnetic resonance images obtained within 1 year VSports最新版本. .
Main outcome measures: We used automated tools to compute annual longitudinal atrophy in the hippocampus and cortical regions targeted in AD. We used Mini-Mental State Examination scores as a measure of cognitive performance V体育平台登录. We performed a cross-subject analysis of atrophy rates and acceleration on individuals with an AD-like cerebrospinal fluid molecular profile. .
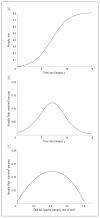
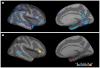
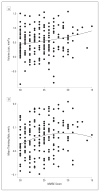
Results: In presymptomatic individuals harboring indicators of AD, baseline thickness in AD-vulnerable cortical regions was significantly reduced compared with that of healthy control individuals, but baseline hippocampal volume was not. Across the clinical spectrum, rates of AD-specific cortical thinning increased with decreasing cognitive performance before peaking at approximately the Mini-Mental State Examination score of 21, beyond which rates of thinning started to decline. Annual rates of hippocampal volume loss showed a continuously increasing pattern with decreasing cognitive performance as low as the Mini-Mental State Examination score of 15. Analysis of the second derivative of imaging measurements revealed that AD-specific cortical thinning exhibited early acceleration followed by deceleration. Conversely, hippocampal volume loss exhibited positive acceleration across all study participants VSports注册入口. .
Conclusions: Alzheimer disease-specific cortical thinning and hippocampal volume loss are consistent with a sigmoidal pattern, with an acceleration phase during the early stages of the disease. Clinical trials should carefully consider the nonlinear behavior of these AD biomarkers. V体育官网入口.
Figures
"V体育安卓版" References
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82(4):239–259. - PubMed
-
- Arnold SE, Hyman BT, Flory J, Damasio AR, Van Hoesen GW. The topographical and neuroanatomical distribution of neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Cereb Cortex. 1991;1(1):103–116. - PubMed
-
- Fox NC, Freeborough PA. Brain atrophy progression measured from registered serial MRI: validation and application to Alzheimer’s disease. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1997;7(6):1069–1075. - PubMed
-
- Fox NC, Scahill RI, Crum WR, Rossor MN. Correlation between rates of brain atrophy and cognitive decline in AD. Neurology. 1999;52(8):1687–1689. - "V体育官网" PubMed
Publication types
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
MeSH terms (VSports app下载)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
Grants and funding
- U24 RR021382/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01EB006758/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS052585-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR014075/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS052585/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- VSports手机版 - RC1 AT005728/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- VSports手机版 - K25 NS069805/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR023043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- "VSports app下载" RC1 AT005728-01/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB006758/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG022381/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- "V体育官网入口" P41-RR14075/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- "VSports手机版" K25 EB013649/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 1KL2RR025757-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States (V体育平台登录)
- VSports - AG022381/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR025757/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States (VSports)
- "VSports最新版本" S10 RR023401/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States

