Phase I (safety) study of autologous tolerogenic dendritic cells in type 1 diabetic patients
- PMID: 21680720
- PMCID: PMC3161299 (VSports注册入口)
- DOI: "V体育2025版" 10.2337/dc11-0472
Phase I (safety) study of autologous tolerogenic dendritic cells in type 1 diabetic patients
Abstract
Objective: The safety of dendritic cells to selectively suppress autoimmunity, especially in type 1 diabetes, has never been ascertained. We investigated the safety of autologous dendritic cells, stabilized into an immunosuppressive state, in established adult type 1 diabetic patients VSports手机版. .
Research design and methods: A randomized, double-blind, phase I study was conducted V体育安卓版. A total of 10, otherwise generally healthy, insulin-requiring type 1 diabetic patients between 18 and 60 years of age, without any other known or suspected health conditions, received autologous dendritic cells, unmanipulated or engineered ex vivo toward an immunosuppressive state. Ten million cells were administered intradermally in the abdomen once every 2 weeks for a total of four administrations. The primary end point determined the proportion of patients with adverse events on the basis of the physician's global assessment, hematology, biochemistry, and immune monitoring for a period of 12 months. .
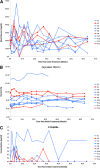
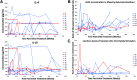
Results: The dendritic cells were safely tolerated. There were no discernible adverse events in any patient throughout the study. Other than a significant increase in the frequency of peripheral B220+ CD11c- B cells, mainly seen in the recipients of engineered dendritic cells during the dendritic cell administration period, there were no statistically relevant differences in other immune populations or biochemical, hematological, and immune biomarkers compared with baseline V体育ios版. .
Conclusions: Treatment with autologous dendritic cells, in a native state or directed ex vivo toward a tolerogenic immunosuppressive state, is safe and well tolerated VSports最新版本. Dendritic cells upregulated the frequency of a potentially beneficial B220+ CD11c- B-cell population, at least in type 1 diabetes autoimmunity. .
Figures
References
-
- Eisenbarth GS. Insulin autoimmunity: immunogenetics/immunopathogenesis of type 1A diabetes. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2003;1005:109–118 - PubMed
-
- Lo J, Clare-Salzler MJ. Dendritic cell subsets and type I diabetes: focus upon DC-based therapy. Autoimmun Rev 2006;5:419–423 - PubMed
-
- McCurry KR, Colvin BL, Zahorchak AF, Thomson AW. Regulatory dendritic cell therapy in organ transplantation. Transpl Int 2006;19:525–538 - PubMed
"V体育ios版" Publication types
- VSports最新版本 - Actions
MeSH terms
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
Substances (VSports注册入口)
Grants and funding
VSports注册入口 - LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
"V体育安卓版" Research Materials

