Loss of downregulated in adenoma (DRA) impairs mucosal HCO3(-) secretion in murine ileocolonic inflammation
- PMID: 21557395
- PMCID: VSports在线直播 - PMC5426909
- DOI: 10.1002/ibd.21744
Loss of downregulated in adenoma (DRA) impairs mucosal HCO3(-) secretion in murine ileocolonic inflammation
Abstract
Background: Ileocolonic luminal pH has been reported to be abnormally low in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients, and one of the causative factors may be reduced epithelial HCO(3)(-) secretory rate (J(HCO3)(-)). Disturbances in J(HCO3)(-) may occur due to inflammation-induced changes in the crypt and villous architecture, or due to the effect of proinflammatory cytokines on epithelial ion transporters VSports手机版. .
Methods: To discriminate between these possibilities, the tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) overexpressing (TNF(+/ΔARE)) mouse model was chosen, which displays high proinflammatory cytokine levels in both ileum and colon, but develops only mild colonic histopathology and diarrhea. HCO(3)(-) secretion, mRNA expression, immunohistochemistry, and fluid absorptive capacity were measured in ileal and mid-colonic mucosa of TNF(+/ΔARE) and wildtype (WT) (TNF(+/+)) mice in Ussing chambers, and in anesthetized mice in vivo V体育安卓版. .
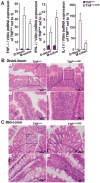
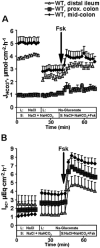
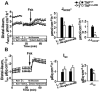
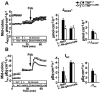
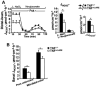
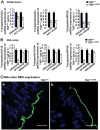
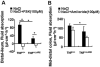
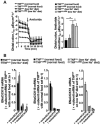
Results: The high basal J(HCO3)(-) observed in WT ileal and mid-colonic mucosa were luminal Cl(-) -dependent and strongly decreased in TNF(+/ΔARE) mice V体育ios版. Downregulated in adenoma (DRA) mRNA and protein expression was strongly decreased in TNF(+/ΔARE) ileocolon, whereas cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), Na(+) /H(+) exchanger 3 (NHE3), Na(+) /HCO(3)(-) cotransporter (NBC), and epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) expression was not significantly altered. This indicates that the severe defect in ileocolonic J(HCO3)(-) was due to DRA downregulation. Fluid absorption was severely depressed in the ileum but only mildly affected in the mid-distal colon, preventing the development of overt diarrhea. .
Conclusions: Even mild ileocolonic inflammation may result in a decrease of epithelial HCO(3)(-) secretion, which may contribute to alterations in surface pH, intestinal flora, and mucus barrier properties VSports最新版本. .
Copyright © 2011 Crohn's & Colitis Foundation of America, Inc V体育平台登录. .
"V体育官网入口" Figures
References
-
- Surawicz CM. Mechanisms of diarrhea. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2010;12:236–241. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz H, Barmeyer C, Fromm M, et al. Altered tight junction structure contributes to the impaired epithelial barrier function in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1999;116:301–309. - PubMed
-
- Seidler U, Lenzen H, Cinar A, et al. Molecular mechanisms of disturbed electrolyte transport in intestinal inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1072:262–275. - PubMed
-
- Greig ER, Mathialahan T, Boot-Handford RP, et al. Molecular and functional studies of electrogenic Na(+) transport in the distal colon and rectum of young and elderly subjects. Gut. 2003;52:1607–1615. - "V体育ios版" PMC - PubMed
-
- Amin MR, Malakooti J, Sandoval R, et al. IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha regulate human NHE3 gene expression by modulating the Sp family transcription factors in human intestinal epithelial cell line C2BBe1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006;291:C887–896. - PubMed
VSports - Publication types
MeSH terms
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- V体育2025版 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
Substances
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
Grants and funding (V体育2025版)
"VSports手机版" LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
