"VSports手机版" Graft-versus-host disease is independent of innate signaling pathways triggered by pathogens in host hematopoietic cells
- PMID: 21098219
- PMCID: PMC5822434
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002965
Graft-versus-host disease is independent of innate signaling pathways triggered by pathogens in host hematopoietic cells
Abstract
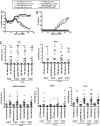
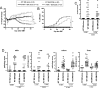
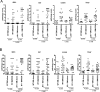
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is initiated by APCs that prime alloreactive donor T cells. In antipathogen responses, Ag-bearing APCs receive signals through pattern-recognition receptors, including TLRs, which induce the expression of costimulatory molecules and production of inflammatory cytokines, which in turn mold the adaptive T cell response. However, in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (alloSCT), there is no specific pathogen, alloantigen is ubiquitous, and signals that induce APC maturation are undefined VSports手机版. To investigate APC activation in GVHD, we used recipient mice with hematopoietic cells genetically deficient in pathways critical for APC maturation in models in which host APCs are absolutely required. Strikingly, CD8-mediated and CD4-mediated GVHD were similar whether host APCs were wild-type or deficient in MyD88, TRIF, or MyD88 and TRIF, which excludes essential roles for TLRs and IL-1β, the key product of inflammasome activation. Th1 differentiation was if anything augmented when APCs were MyD88/TRIF(-/-), and T cell production of IFN-γ did not require host IL-12. GVHD was also intact when APCs lacked the type I IFNR, which amplifies APC activation pathways that induce type I IFNs. Thus in GVHD, alloreactive T cells can be activated when pathways critical for antipathogen T cell responses are impaired. .
Figures

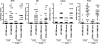


"VSports在线直播" References
-
- Shlomchik WD. Graft-versus-host disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:340–352. - PubMed
-
- Teshima T, Ordemann R, Reddy P, Gagin S, Liu C, Cooke KR, Ferrara JL. Acute graft-versus-host disease does not require alloantigen expression on host epithelium. Nat Med. 2002;8:575–581. - PubMed
-
- Duffner UA, Maeda Y, Cooke KR, Reddy P, Ordemann R, Liu C, Ferrara JL, Teshima T. Host dendritic cells alone are sufficient to initiate acute graft-versus-host disease. J Immunol. 2004;172:7393–7398. - PubMed
-
- Koyama M, Hashimoto D, Aoyama K, Matsuoka K, Karube K, Niiro H, Harada M, Tanimoto M, Akashi K, Teshima T. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells prime alloreactive T cells to mediate graft-versus-host disease as antigen-presenting cells. Blood. 2009;113:2088–2095. - PubMed (V体育安卓版)
-
- Matte CC, Liu J, Cormier J, Anderson BE, Athanasiadis I, Jain D, McNiff J, Shlomchik WD. Donor APCs are required for maximal GVHD but not for GVL. Nat Med. 2004;10:987–992. - PubMed
Publication types
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- VSports - Actions
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (V体育官网)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "VSports最新版本" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
Substances (V体育安卓版)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources (V体育2025版)
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
"V体育安卓版" Research Materials
Miscellaneous

