VSports注册入口 - Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor drives the in vitro differentiation of human dendritic cells that induce anergy in naïve T cells
- PMID: 20957751
- PMCID: PMC2997328
- DOI: 10.1002/eji.201040659
Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor drives the in vitro differentiation of human dendritic cells that induce anergy in naïve T cells
Abstract (VSports)
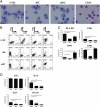
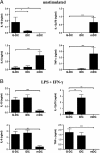
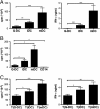
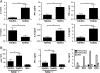
G-CSF is a modulator of T-cell and DC functions. Previous reports show that monocytes from G-CSF-treated (post-G) healthy donors differentiate into tolerogenic DC in vitro in the presence of autologous serum, containing high levels of IL-10 and IFN-α, and in turn induce type 1 Treg (Tr1) cells. However, the direct effect of G-CSF on DC differentiation was not investigated. Here, we show that monocytes differentiated in the presence of exogenous G-CSF (G-DC) remain CD14(+) CD1a(-) , but acquire a DC-like morphology, express CD83 and CD86 and low levels of the tolerogenic markers Ig-like transcript (ILT)4 and HLA-G. G-DC spontaneously produce IL-10 and, upon stimulation, low levels of IL-12. G-DC display low stimulatory capacity and induce anergy in naïve T cells, but do not confer suppressive function. Therefore, in vitro differentiation of monocyte-derived DC in the presence of G-CSF can replicate some but not all features of post-G DC VSports手机版. These findings indicate that the tolerogenic properties of G-CSF do not exclusively reside in its direct effect on DC, which in turn induce T-cell anergy, but also in its ability to generate a tolerogenic milieu in vivo, which is necessary for Tr1 cell induction and cannot be replicated in vitro. .
Copyright © 2010 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co V体育安卓版. KGaA, Weinheim. .
Figures

References
-
- Demetri GD, Griffin JD. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and its receptor. Blood. 1991;78:2791–2808. - PubMed
-
- Liongue C, Wright C, Russell AP, Ward AC. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor: stimulating granulopoiesis and much more. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009;41:2372–2375. - PubMed
-
- Sloand EM, Kim S, Maciejewski JP, Van Rhee F, Chaudhuri A, Barrett J, Young NS. Pharmacologic doses of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor affect cytokine production by lymphocytes in vitro and in vivo. Blood. 2000;95:2269–2274. - PubMed
-
- Franzke A, Piao W, Lauber J, Gatzlaff P, Konecke C, Hansen W, Schmitt-Thomsen A, et al. G-CSF as immune regulator in T cells expressing the G-CSF receptor: implications for transplantation and autoimmune diseases. Blood. 2003;102:734–739. - PubMed
-
- Morikawa K, Morikawa S, Nakamura M, Miyawaki T. Characterization of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor expressed on human lymphocytes. Br. J. Haematol. 2002;118:296–304. - PubMed (V体育官网入口)
Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (VSports)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "V体育官网" Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
V体育安卓版 - Substances
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "V体育安卓版" Actions
- "V体育ios版" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources (V体育安卓版)
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources (V体育安卓版)
Research Materials

