Gene expression profiling of blood for the prediction of ischemic stroke
- PMID: 20798371
- PMCID: PMC2987675
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.588335
Gene expression profiling of blood for the prediction of ischemic stroke (V体育2025版)
Abstract
Background and purpose: A blood-based biomarker of acute ischemic stroke would be of significant value in clinical practice. This study aimed to (1) replicate in a larger cohort our previous study using gene expression profiling to predict ischemic stroke; and (2) refine prediction of ischemic stroke by including control groups relevant to ischemic stroke. VSports手机版.
Methods: Patients with ischemic stroke (n=70, 199 samples) were compared with control subjects who were healthy (n=38), had vascular risk factors (n=52), and who had myocardial infarction (n=17). Whole blood was drawn ≤3 hours, 5 hours, and 24 hours after stroke onset and from control subjects V体育安卓版. RNA was processed on whole genome microarrays. Genes differentially expressed in ischemic stroke were identified and analyzed for predictive ability to discriminate stroke from control subjects. .
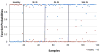
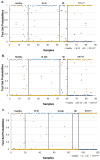
Results: The 29 probe sets previously reported predicted a new set of ischemic strokes with 93. 5% sensitivity and 89 V体育ios版. 5% specificity. Sixty- and 46-probe sets differentiated control groups from 3-hour and 24-hour ischemic stroke samples, respectively. A 97-probe set correctly classified 86% of ischemic strokes (3 hour+24 hour), 84% of healthy subjects, 96% of vascular risk factor subjects, and 75% with myocardial infarction. .
Conclusions: This study replicated our previously reported gene expression profile in a larger cohort and identified additional genes that discriminate ischemic stroke from relevant control groups. This multigene approach shows potential for a point-of-care test in acute ischemic stroke VSports最新版本. .
Figures
References
-
- Tang Y, Xu H, Du X, Lit L, Walker W, Lu A, Ran R, Gregg JP, Reilly M, Pancioli A, Khoury JC, Sauerbeck LR, Carrozzella JA, Spilker J, Clark J, Wagner KR, Jauch EC, Chang DJ, Verro P, Broderick JP, Sharp FR. Gene expression in blood changes rapidly in neutrophils and monocytes after ischemic stroke in humans: A microarray study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006;26:1089–1102. - PubMed
-
- Thom T, Haase N, Rosamond W, Howard VJ, Rumsfeld J, Manolio T, Zheng ZJ, Flegal K, O’Donnell C, Kittner S, Lloyd-Jones D, Goff DC, Jr, Hong Y, Adams R, Friday G, Furie K, Gorelick P, Kissela B, Marler J, Meigs J, Roger V, Sidney S, Sorlie P, Steinberger J, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Wilson M, Wolf P. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2006 update: A report from the american heart association statistics committee and stroke statistics subcommittee. Circulation. 2006;113:e85–151. - PubMed
-
- WHO. The atlas of heart disease and stroke. 2005
-
- Whiteley W, Tseng MC, Sandercock P. Blood biomarkers in the diagnosis of ischemic stroke: A systematic review. Stroke. 2008;39:2902–2909. - PubMed
Publication types (VSports注册入口)
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
MeSH terms
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- VSports - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- V体育官网 - Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
"VSports app下载" Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

