"VSports" Autophagy facilitates IFN-gamma-induced Jak2-STAT1 activation and cellular inflammation
- PMID: 20592027
- PMCID: "VSports在线直播" PMC2937899
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.133355 (V体育官网入口)
Autophagy facilitates IFN-gamma-induced Jak2-STAT1 activation and cellular inflammation
Abstract
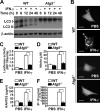
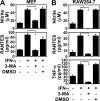
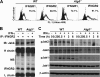
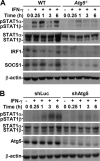
Autophagy is regulated for IFN-gamma-mediated antimicrobial efficacy; however, its molecular effects for IFN-gamma signaling are largely unknown. Here, we show that autophagy facilitates IFN-gamma-activated Jak2-STAT1. IFN-gamma induces autophagy in wild-type but not in autophagy protein 5 (Atg5(-/-))-deficient mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), and, autophagy-dependently, IFN-gamma induces IFN regulatory factor 1 and cellular inflammatory responses. Pharmacologically inhibiting autophagy using 3-methyladenine, a known inhibitor of class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, confirms these effects VSports手机版. Either Atg5(-/-) or Atg7(-/-) MEFs are, independent of changes in IFN-gamma receptor expression, resistant to IFN-gamma-activated Jak2-STAT1, which suggests that autophagy is important for IFN-gamma signal transduction. Lentivirus-based short hairpin RNA for Atg5 knockdown confirmed the importance of autophagy for IFN-gamma-activated STAT1. Without autophagy, reactive oxygen species increase and cause SHP2 (Src homology-2 domain-containing phosphatase 2)-regulated STAT1 inactivation. Inhibiting SHP2 reversed both cellular inflammation and the IFN-gamma-induced activation of STAT1 in Atg5(-/-) MEFs. Our study provides evidence that there is a link between autophagy and both IFN-gamma signaling and cellular inflammation and that autophagy, because it inhibits the expression of reactive oxygen species and SHP2, is pivotal for Jak2-STAT1 activation. .
Figures
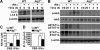

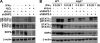
References
-
- Delgado M. A., Elmaoued R. A., Davis A. S., Kyei G., Deretic V. (2008) EMBO J. 27, 1110–1121 - PMC (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
-
- Codogno P., Meijer A. J. (2005) Cell Death Differ. 12, (Suppl. 2), 1509–1518 - PubMed
-
- Lee H. K., Lund J. M., Ramanathan B., Mizushima N., Iwasaki A. (2007) Science 315, 1398–1401 - PubMed
-
- English L., Chemali M., Duron J., Rondeau C., Laplante A., Gingras D., Alexander D., Leib D., Norbury C., Lippé R., Desjardins M. (2009) Nat. Immunol. 10, 480–487 - PMC (VSports最新版本) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- V体育平台登录 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网)
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- VSports注册入口 - Actions
- "V体育官网入口" Actions
Substances
- V体育官网 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (VSports app下载)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

