Identification of GATA6 sequence variants in patients with congenital heart defects
- PMID: 20581743
- PMCID: V体育官网 - PMC2940936
- DOI: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e3181ed17e4 (V体育官网)
"V体育2025版" Identification of GATA6 sequence variants in patients with congenital heart defects
Abstract
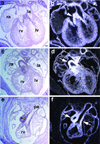
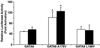
Although the etiology for the majority of congenital heart disease (CHD) remains poorly understood, the known genetic causes are often the result of mutations in cardiac developmental genes. GATA6 encodes for a cardiac transcription factor, which is broadly expressed in the developing heart and is critical for normal cardiac morphogenesis, making it a candidate gene for congenital heart defects in humans. The objective of this study was to determine the frequency of GATA6 sequence variants in a population of individuals with a spectrum of cardiac malformations. The coding regions of GATA6 were sequenced in 310 individuals with CHD. We identified two novel sequence variations in GATA6 that altered highly conserved amino acid residues (A178V and L198V) and were not found in a control population VSports手机版. These variants were identified in two individuals (one with tetralogy of Fallot and the other with an atrioventricular septal defect in the setting of complex CHD). Biochemical studies demonstrate that the GATA6 A178V mutant protein results in increased transactivation ability when compared with wild-type GATA6. These data suggest that nonsynonymous GATA6 sequence variants are infrequently found in individuals with CHD. .
Figures

References
-
- Hoffman JI, Kaplan S. The incidence of congenital heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39:1890–1900. - PubMed (VSports)
-
- Ransom J, Srivastava D. The genetics of cardiac birth defects. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2007;18:132–139. - PubMed
-
- Garg V, Kathiriya IS, Barnes R, Schluterman MK, King IN, Butler CA, Rothrock CR, Eapen RS, Hirayama-Yamada K, Joo K, Matsuoka R, Cohen JC, Srivastava D. GATA4 mutations cause human congenital heart defects and reveal an interaction with TBX 5. Nature. 2003;424:443–447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms (VSports最新版本)
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- "V体育官网" Actions
- V体育官网入口 - Actions
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- Actions (V体育官网入口)
- Actions (V体育安卓版)
- "V体育2025版" Actions
- V体育ios版 - Actions
- Actions (V体育ios版)
"VSports最新版本" Substances
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (V体育2025版)
V体育官网 - Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

