PPARalpha: energy combustion, hypolipidemia, inflammation and cancer (V体育安卓版)
- PMID: 20414453
- PMCID: PMC2858266
- DOI: 10.1621/nrs.08002
PPARalpha: energy combustion, hypolipidemia, inflammation and cancer
Abstract
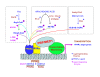
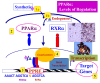
The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha, or NR1C1) is a nuclear hormone receptor activated by a structurally diverse array of synthetic chemicals known as peroxisome proliferators VSports手机版. Endogenous activation of PPARalpha in liver has also been observed in certain gene knockout mouse models of lipid metabolism, implying the existence of enzymes that either generate (synthesize) or degrade endogenous PPARalpha agonists. For example, substrates involved in fatty acid oxidation can function as PPARalpha ligands. PPARalpha serves as a xenobiotic and lipid sensor to regulate energy combustion, hepatic steatosis, lipoprotein synthesis, inflammation and liver cancer. Mainly, PPARalpha modulates the activities of all three fatty acid oxidation systems, namely mitochondrial and peroxisomal beta-oxidation and microsomal omega-oxidation, and thus plays a key role in energy expenditure. Sustained activation of PPARalpha by either exogenous or endogenous agonists leads to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma resulting from sustained oxidative and possibly endoplasmic reticulum stress and liver cell proliferation. PPARalpha requires transcription coactivator PPAR-binding protein (PBP)/mediator subunit 1(MED1) for its transcriptional activity. .
Figures

References
-
- Antonson P., Schuster G. U., Wang L., Rozell B., Holter E., Flodby P., Treuter E., Holmgren L., Gustafsson J. A. Inactivation of the nuclear receptor coactivator RAP250 in mice results in placental vascular dysfunction. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:1260–8. - PMC (VSports在线直播) - PubMed
-
- Aoyama T., Peters J. M., Iritani N., Nakajima T., Furihata K., Hashimoto T., Gonzalez F. J. Altered constitutive expression of fatty acid-metabolizing enzymes in mice lacking the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARalpha) J Biol Chem. 1998;273:5678–84. - PubMed
-
- Arzuaga X., Reiterer G., Majkova Z., Kilgore M. W., Toborek M., Hennig B. PPARalpha ligands reduce PCB-induced endothelial activation: possible interactions in inflammation and atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2007;7:264–72. - PubMed
-
- Barger P. M., Browning A. C., Garner A. N., Kelly D. P. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α: a potential role in the cardiac metabolic stress response. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:44495–501. - VSports - PubMed
-
- Bays H., Stein E. A. Pharmacotherapy for dyslipidaemia--current therapies and future agents. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2003;4:1901–38. - PubMed
"VSports手机版" Publication types
MeSH terms
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
- "VSports手机版" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- VSports app下载 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
Substances
- Actions (VSports)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
"V体育官网入口" Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous (VSports注册入口)

