DNase I inhibits a late phase of reactive oxygen species production in neutrophils
- PMID: 20375609
- PMCID: PMC2919508
- DOI: 10.1159/000235860 (V体育官网)
DNase I inhibits a late phase of reactive oxygen species production in neutrophils
Abstract
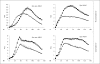
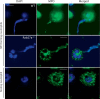
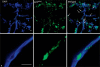
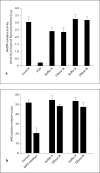
Neutrophils kill bacteria on extracellular complexes of DNA fibers and bactericidal proteins known as neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). The NET composition and the bactericidal mechanisms they use are not fully understood. Here, we show that treatment with deoxyribonuclease (DNase I) impairs a late oxidative response elicited by Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and also by phorbol ester. Isoluminol-dependent chemiluminescence elicited by opsonized Listeria monocytogenes-stimulated neutrophils was inhibited by DNase I, and the DNase inhibitory effect was also evident when phagocytosis was blocked, suggesting that DNase inhibits an extracellular mechanism of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. The DNase inhibitory effect was independent of actin polymerization VSports手机版. Phagocytosis and cell viability were not impaired by DNase I. Immunofluorescence analysis shows that myeloperoxidase is present on NETs. Furthermore, granular proteins were detected in NETs from Rab27a-deficient neutrophils which have deficient exocytosis, suggesting that exocytosis and granular protein distribution on NETs proceed by independent mechanisms. NADPH oxidase subunits were also detected on NETs, and the detection of extracellular trap-associated NADPH oxidase subunits was abolished by treatment with DNase I and dependent on cell stimulation. In vitro analyses demonstrate that MPO and NADPH oxidase activity are not directly inhibited by DNase I, suggesting that its effect on ROS production depends on NET disassembly. Altogether, our data suggest that inhibition of ROS production by microorganism-derived DNase would contribute to their ability to evade killing. .
(c) 2009 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures



References
-
- Reeves EP, Lu H, Jacobs HL, Messina CG, Bolsover S, Gabella G, Potma EO, Warley A, Roes J, Segal AW. Killing activity of neutrophils is mediated through activation of proteases by K+ flux. Nature. 2002;416:291–297. - PubMed
-
- Babior BM. NADPH oxidase. Curr Opin Immunol. 2004;16:42–47. - "V体育官网" PubMed
-
- Urban CF, Lourido S, Zychlinsky A. How do microbes evade neutrophil killing? Cell Microbiol. 2006;8:1687–1696. - PubMed
-
- Brinkmann V, Reichard U, Goosmann C, Fauler B, Uhlemann Y, Weiss DS, Weinrauch Y, Zychlinsky A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science. 2004;303:1532–1535. - PubMed
-
- Buchanan JT, Simpson AJ, Aziz RK, Liu GY, Kristian SA, Kotb M, Feramisco J, Nizet V. DNase expression allows the pathogen group A Streptococcus to escape killing in neutrophil extracellular traps. Curr Biol. 2006;16:396–400. - PubMed
"V体育ios版" Publication types
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports最新版本)
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- V体育官网 - Actions
- "VSports在线直播" Actions
Substances
- Actions (V体育官网)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous (VSports)

