A distinct subset of proinflammatory neutrophils isolated from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus induces vascular damage and synthesizes type I IFNs
- PMID: 20164424
- PMCID: PMC2929645 (V体育官网入口)
- DOI: "V体育官网入口" 10.4049/jimmunol.0902199
A distinct subset of proinflammatory neutrophils isolated from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus induces vascular damage and synthesizes type I IFNs
Erratum in
- J Immunol. 2010 Sep 15;185(6):3779
Abstract
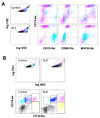
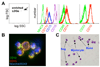
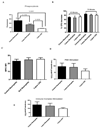
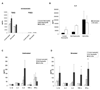
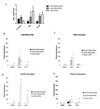
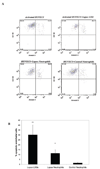
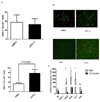
Neutrophil-specific genes are abundant in PBMC microarrays from lupus patients because of the presence of low-density granulocytes (LDGs) in mononuclear cell fractions. The functionality and pathogenicity of these LDGs have not been characterized. We developed a technique to purify LDGs from lupus PBMCs and assessed their phenotype, function, and potential role in disease pathogenesis. LDGs, their autologous lupus neutrophils, and healthy control neutrophils were compared with regard to their microbicidal and phagocytic capacities, generation of reactive oxygen species, activation status, inflammatory cytokine profile, and type I IFN expression and signatures. The capacity of LDGs to kill endothelial cells and their antiangiogenic potential were also assessed. LDGs display an activated phenotype, secrete increased levels of type I IFNs, TNF-alpha, and IFN-gamma, but show impaired phagocytic potential. LDGs induce significant endothelial cell cytotoxicity and synthesize sufficient levels of type I IFNs to disrupt the capacity of endothelial progenitor cells to differentiate into mature endothelial cells. LDG depletion restores the functional capacity of endothelial progenitor cells. We conclude that lupus LDGs are proinflammatory and display pathogenic features, including the capacity to synthesize type I IFNs. They may play an important dual role in premature cardiovascular disease development in systemic lupus erythematosus by simultaneously mediating enhanced vascular damage and inhibiting vascular repair. VSports手机版.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kyttaris VC, Juang YT, Tsokos GC. Immune cells and cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus: an update. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2005;17:518–522. - PubMed
-
- Denny MF, Chandaroy P, Killen PD, Caricchio R, Lewis EE, Richardson BC, Lee KD, Gavalchin J, Kaplan MJ. Accelerated macrophage apoptosis induces autoantibody formation and organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 2006;176:2095–2104. - PubMed
-
- Banchereau J, Pascual V. Type I interferon in systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases. Immunity. 2006;25:383–392. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan MJ, Lewis EE, Shelden EA, Somers E, Pavlic R, McCune WJ, Richardson BC. The apoptotic ligands TRAIL, TWEAK, and Fas ligand mediate monocyte death induced by autologous lupus T cells. J Immunol. 2002;169:6020–6029. - PubMed
"V体育2025版" Publication types
- Actions (VSports)
MeSH terms
- Actions (VSports注册入口)
- Actions (VSports app下载)
- "VSports" Actions
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- VSports在线直播 - Actions
- Actions (V体育平台登录)
- "V体育平台登录" Actions
- "VSports" Actions
- Actions (VSports在线直播)
- "VSports app下载" Actions
"V体育平台登录" Substances
- "VSports注册入口" Actions
- V体育安卓版 - Actions
V体育2025版 - Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

